- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Fish Oil: A Heart-Healthy Supplement for Managing Blood Pressure
2025-05-25
Incorporating fish oil into your diet or using it as a supplement may assist in lowering high blood pressure, defined as readings consistently above 130/80 mm Hg. High blood pressure, or hypertension, arises when excessive pressure is exerted on artery walls.
Fish Oil's Role in Blood Pressure Management
Research increasingly supports the notion that fish oil can beneficially impact blood pressure. Interest in fish oil's cardiovascular benefits emerged in the 1970s when scientists observed that populations with high fish consumption, such as those in Japan and Greenland, exhibited lower incidences of heart attacks.
A 2023 meta-analysis reviewing eight studies focused on omega-3 supplements and blood pressure among individuals with metabolic syndrome—an assortment of symptoms heightening the risk for chronic conditions like heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. The findings indicated that omega-3 intake led to lowered systolic and diastolic blood pressure, alongside improved cholesterol levels.
Defining Fish Oil
Fish oil, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, originates from the tissues of certain fatty, cold-water fish and boasts numerous health advantages. It contains eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Sources of fish oil include supplements or consumption of fish such as salmon, tuna, or mackerel. Experts advise adults to eat 8 ounces of seafood weekly.
Recommended Dosage
There's no official guideline for daily fish oil consumption to achieve health benefits, but research suggests that omega-3 doses of 2-3 grams per day over approximately 10 weeks can significantly lower blood pressure. While larger doses might offer additional benefits, studies focused on omega-3 fatty acids rather than specific fish oil supplements.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
Fish oil supplements typically yield minimal side effects, with the most common being an unpleasant taste or "fishy" breath. Using capsules with Lemon Extract or other flavor additives can mitigate these effects. Other possible side effects include diarrhea, headache, heartburn, and nausea. Choosing high-quality fish oil supplements is crucial, as the FDA does not strictly regulate them. Opt for supplements that have undergone third-party testing and possess sustainability certifications.
Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Blood Pressure
Maintaining optimal blood pressure involves several lifestyle strategies, including: eating a balanced diet, regular exercise, limiting alcohol and sodium intake, managing stress, and quitting smoking.
The Importance of Addressing High Blood Pressure
Treating high blood pressure is vital, as neglecting it can elevate the risk of heart attack, heart disease, heart failure, kidney disease, sexual dysfunction, stroke, and vision loss. Consult with a healthcare provider before introducing any new supplements and avoid self-treatment for high blood pressure. While lifestyle changes can help manage blood pressure, some individuals may need medication to maintain safe levels.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
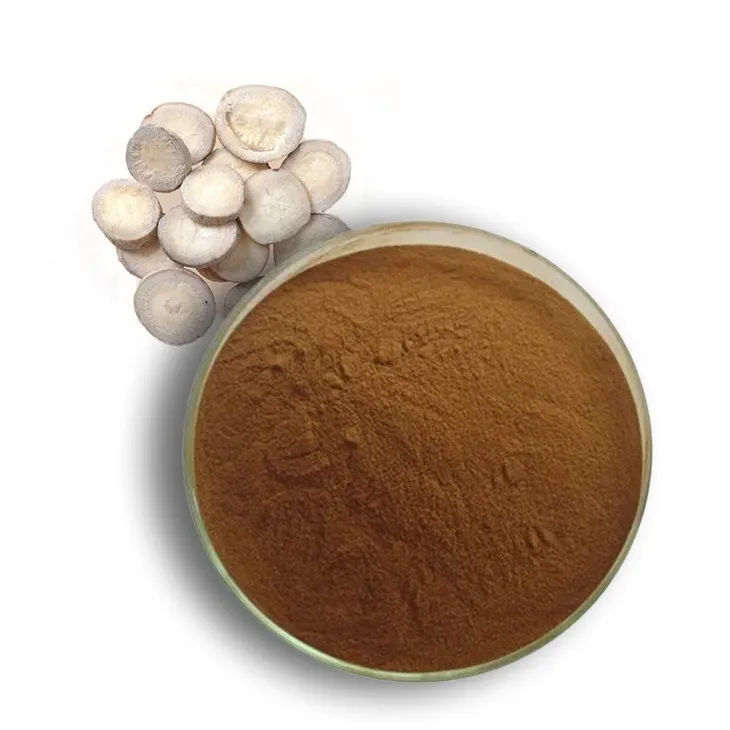
White Peony Extract
2025-05-25
-
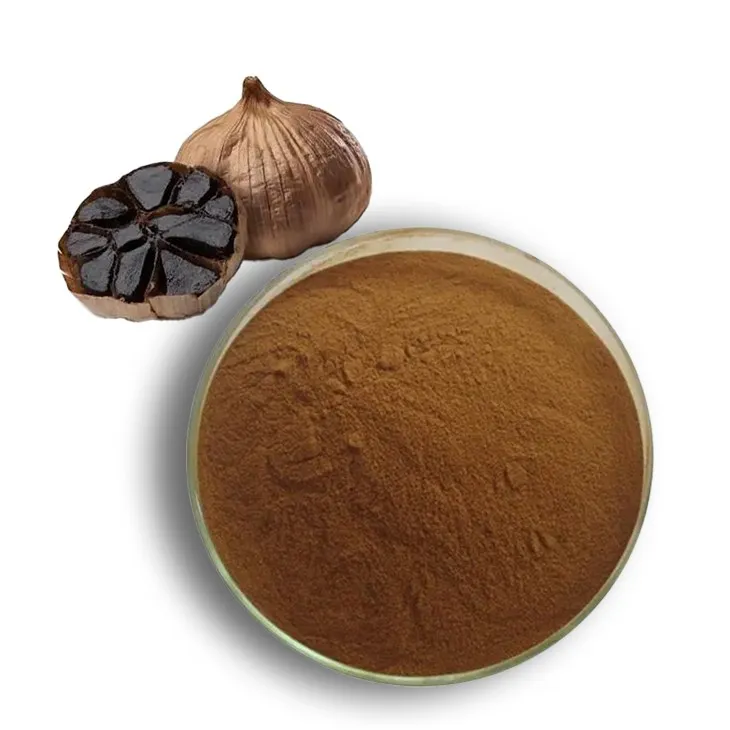
Black Garlic Extract
2025-05-25
-
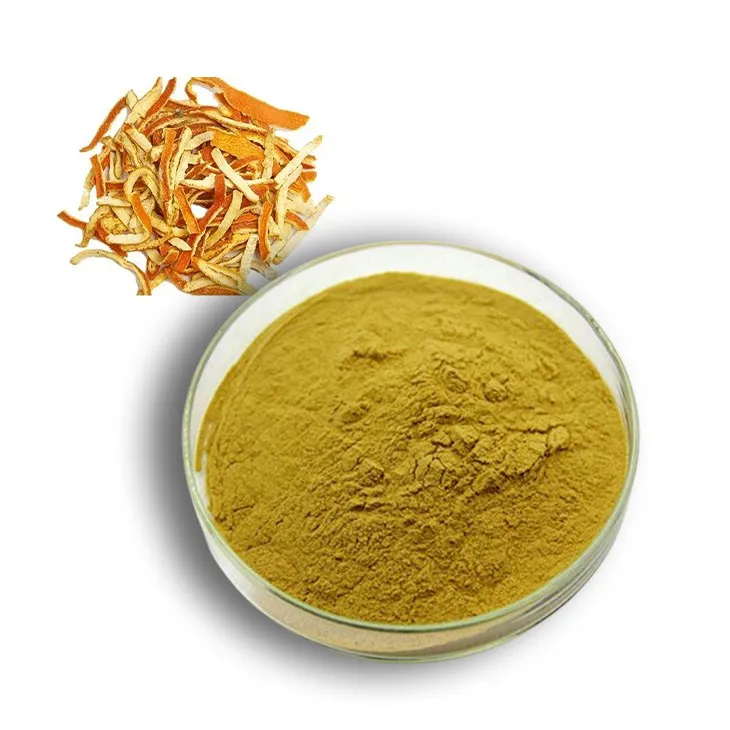
Hesperidin
2025-05-25
-
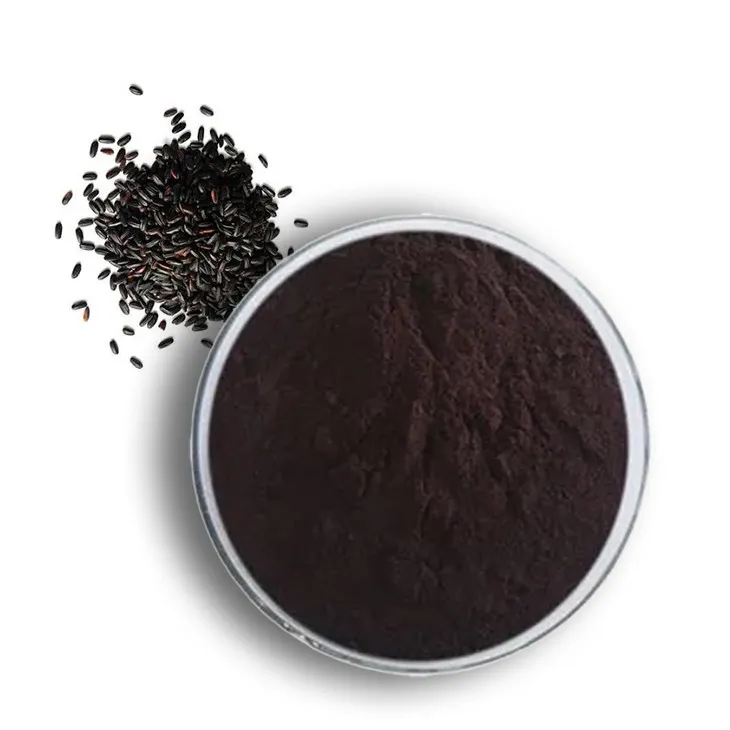
Black Rice Extract
2025-05-25
-
Maca Extract
2025-05-25
-
Astaxanthin
2025-05-25
-
Chaste Berry Extract
2025-05-25
-
Tongkat Ali Extract Powder
2025-05-25
-
Citrus Aurantium Extract
2025-05-25
-
Mangosteen extract powder
2025-05-25