- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
When to Use Astaxanthin
2025-10-31
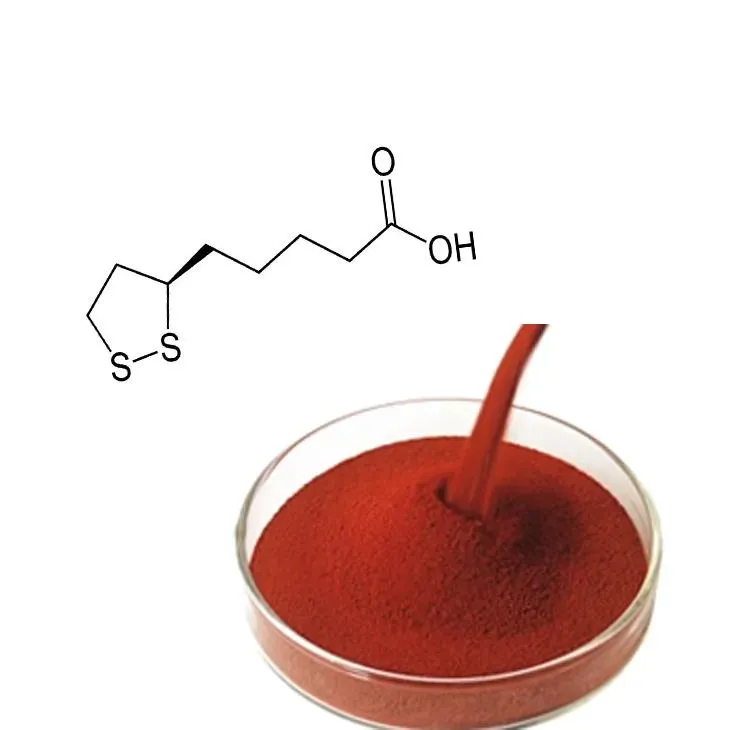
Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid found in marine organisms such as microalgae, shrimp, krill, and salmon. Known for its vibrant red-orange pigment, this compound has gained significant attention in the health and wellness world for its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Unlike other antioxidants, Astaxanthin can cross the blood-brain barrier and cell membranes, making it uniquely effective in protecting cells throughout the body.
But when exactly should one consider using Astaxanthin, and what health benefits can it provide? Let’s explore the scientific evidence and practical applications of this powerful supplement.
What Is Astaxanthin and How Does It Work?
Before understanding when to use astaxanthin, it is essential to grasp its underlying mechanisms.
How Is Astaxanthin Different from Other Antioxidants?
Astaxanthin belongs to the carotenoid family, which includes beta-carotene, lutein, and Lycopene. What sets astaxanthin apart is its ability to neutralize free radicals both inside and outside of the cell. It protects lipids, proteins, and DNA from oxidative damage more effectively than vitamin C, vitamin E, and coenzyme Q10.
Additionally, astaxanthin has anti-inflammatory properties. It inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and supports healthy immune function, which makes it useful in combating chronic inflammation and oxidative stress-related conditions.
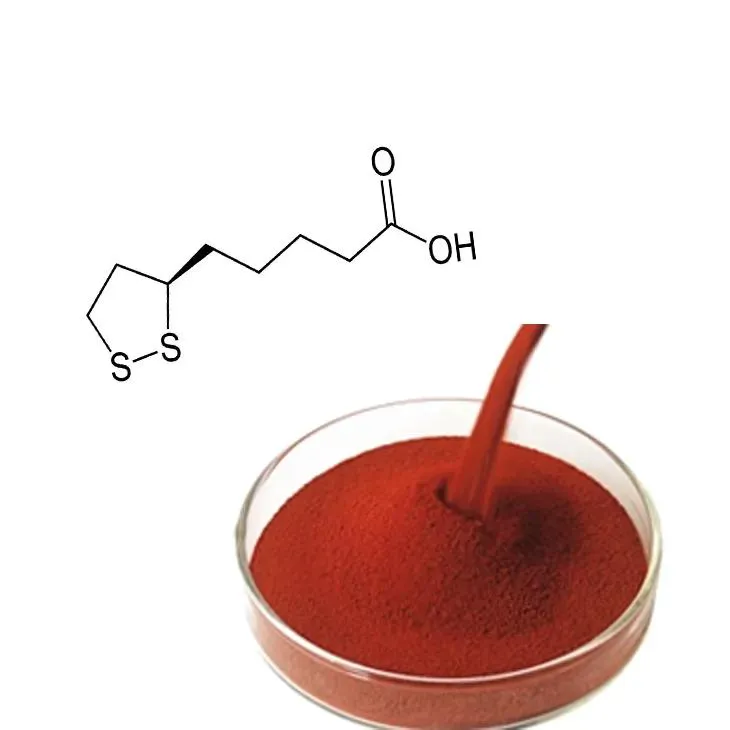
When Should You Use Astaxanthin for Skin Health?
Astaxanthin has gained popularity in dermatology and skincare due to its ability to protect against photoaging and oxidative skin damage.
Can Astaxanthin Protect Against UV Damage?
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight generates free radicals in the skin, which accelerates aging, causes wrinkles, and increases the risk of skin cancer. Astaxanthin neutralizes these free radicals and reduces oxidative stress in skin cells.
Clinical studies indicate that regular supplementation of astaxanthin can improve skin elasticity, hydration, and overall texture, while reducing fine lines and age spots. It can be taken orally in capsule form or applied topically in certain skincare formulations.
When Should You Start Taking Astaxanthin for Anti-Aging?
For individuals in their late 20s or early 30s, astaxanthin can serve as a preventive supplement to combat oxidative stress and maintain skin health. Those with early signs of aging, frequent sun exposure, or environmental stressors may also benefit from starting supplementation sooner.

When Is Astaxanthin Useful for Eye Health?
The eyes are particularly susceptible to oxidative damage due to high exposure to light and oxygen. Astaxanthin supports ocular health and visual performance.
How Can Astaxanthin Protect Vision?
Astaxanthin crosses the blood-retina barrier, allowing it to reach the eyes directly. It helps reduce eye strain, fatigue, and inflammation, especially in individuals who spend long hours in front of digital screens.
Studies suggest that astaxanthin may improve visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and retinal blood flow. It may also protect against age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts by counteracting oxidative stress in the eye.
When Should You Take It for Eye Fatigue?
Individuals experiencing digital eye strain, prolonged computer use, or night driving fatigue may consider daily supplementation of astaxanthin. It is particularly useful for professionals in front of screens or for people over 40, when age-related oxidative damage can begin to accumulate.
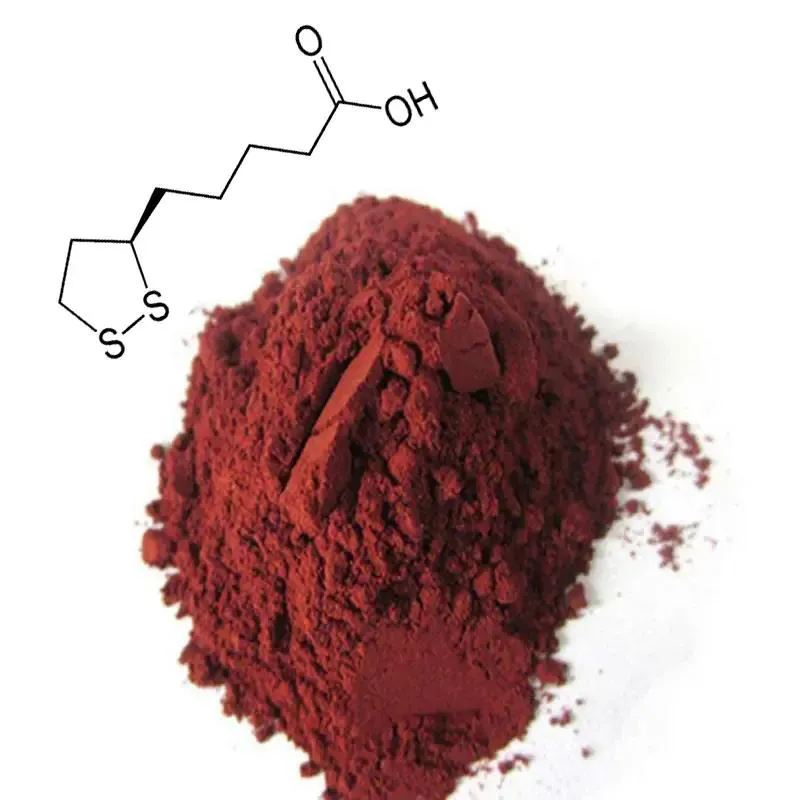
When to Use Astaxanthin for Athletic Performance
Athletes and active individuals have turned to astaxanthin for its ability to enhance endurance and recovery.
Can Astaxanthin Improve Exercise Performance?
Intense exercise generates oxidative stress, leading to muscle fatigue, inflammation, and delayed recovery. Astaxanthin’s antioxidant properties help reduce muscle damage, improve energy metabolism, and enhance endurance.
Research shows that supplementation can increase oxygen utilization and reduce lactic acid buildup during workouts. It may also support joint health and minimize exercise-induced inflammation.
When Is the Best Time to Take It for Sports Performance?
For optimal benefits, athletes may take astaxanthin daily, several weeks before intensive training or competition. Consistent use helps protect muscles from oxidative damage and may improve overall performance and recovery over time.
When Should Astaxanthin Be Used for Heart Health?
Cardiovascular disease remains one of the leading causes of morbidity worldwide. Oxidative stress and inflammation are major contributors to heart disease, and astaxanthin offers protective cardiovascular effects.
How Does Astaxanthin Support Heart Health?
Astaxanthin helps reduce LDL cholesterol oxidation, improve endothelial function, and support healthy blood lipid levels. Its anti-inflammatory properties also reduce vascular inflammation, which is a key factor in atherosclerosis.
Clinical studies suggest that regular supplementation may improve blood pressure regulation, arterial flexibility, and overall cardiovascular resilience.
Who Should Consider Astaxanthin for Heart Protection?
Adults over 40, individuals with high cholesterol, mild hypertension, or a family history of heart disease may benefit from incorporating astaxanthin into their daily regimen as a preventive measure.
When Is Astaxanthin Useful for Brain Health?
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain. Astaxanthin’s ability to cross the blood-brain barrier makes it particularly effective for cognitive support.
How Can It Improve Cognitive Function?
Astaxanthin helps protect neurons from oxidative damage, reduce inflammation, and improve cerebral blood flow. Preliminary research suggests it may enhance memory, learning, and mental clarity, particularly in older adults.
When Should You Start Taking It for Brain Health?
Individuals experiencing age-related cognitive decline, mental fatigue, or high stress may benefit from early supplementation. Regular use over months is recommended for noticeable improvements in cognitive performance and neuroprotection.
When to Use Astaxanthin for Immune Support
A robust immune system relies on proper antioxidant defense to combat pathogens and regulate inflammation. Astaxanthin plays a critical role in modulating immune responses.
How Does Astaxanthin Enhance Immunity?
Astaxanthin enhances natural killer (NK) cell activity, supports T-cell function, and reduces chronic inflammation that can impair immune function. It also protects immune cells from oxidative stress, improving overall resilience against infections.
When Should You Take It to Boost Immunity?
During cold and flu season, periods of high stress, or post-illness recovery, astaxanthin supplementation may help strengthen the body’s natural defenses. Athletes or individuals undergoing intense physical training may also benefit due to temporary immune suppression caused by rigorous exercise.
When Is Astaxanthin Beneficial for Joint and Muscle Health?
Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to joint pain, stiffness, and muscle degradation over time. Astaxanthin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it a natural option for musculoskeletal health.
Can Astaxanthin Reduce Arthritis Symptoms?
Preliminary studies suggest that astaxanthin can reduce joint pain and stiffness, improve mobility, and decrease markers of inflammation in conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
When Should You Start Supplementing for Joint Support?
Adults experiencing early signs of joint discomfort, chronic pain, or inflammation due to age or physical activity may benefit from regular astaxanthin supplementation. Consistent use over several weeks to months often yields noticeable improvements.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Astaxanthin?
The optimal dosage of astaxanthin varies depending on the intended use, but most studies recommend 4–12 mg per day for general health benefits. For specific conditions like cardiovascular support, skin health, or cognitive protection, doses may range up to 12 mg daily under professional guidance.
Astaxanthin is best absorbed when taken with dietary fats, as it is a fat-soluble compound. Regular daily supplementation is advised to achieve consistent antioxidant effects.
Are There Any Side Effects or Precautions?
Astaxanthin is generally well-tolerated, with rare side effects including mild gastrointestinal discomfort or skin discoloration at very high doses.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a healthcare provider before use.
Individuals taking medications for blood pressure, cholesterol, or anticoagulation should seek medical advice to avoid potential interactions.
Astaxanthin is considered safe for long-term use when taken within recommended dosages.
Conclusion: When Should You Use Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a versatile and potent antioxidant suitable for skin protection, eye health, brain support, cardiovascular wellness, immune modulation, athletic performance, and joint health. Its ability to cross cell membranes and the blood-brain barrier gives it unique advantages over other antioxidants.
The optimal timing for use depends on your specific goals:
Skin and anti-aging: Early adulthood to midlife, or during periods of high sun exposure.
Eye health: For digital eye strain, prolonged screen time, or age-related visual decline.
Athletic performance: Prior to intensive training or ongoing for recovery.
Heart and brain health: Middle age or older, or for individuals with risk factors.
Immune support: During stress, illness recovery, or seasonal changes.
Joint and muscle health: At the first sign of discomfort or chronic inflammation.
By integrating astaxanthin into a balanced lifestyle and diet, it can serve as a powerful ally in maintaining overall wellness and protecting against oxidative stress in multiple systems of the body.
Visit Greenskybio.com, a great article source where you can learn about Supplements and their health benefits, you also can get the latest food Supplements. Green Sky Bio provides the best extracts and supplements. It is a Chinese self-developed brand that is trustworthy! Welcome to email us to inquire about our products.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Tongkat Ali Extract Powder
2025-10-31
-
Phyllanthus Emblica Extract
2025-10-31
-
Kelp Extract Powder
2025-10-31
-
Cactus Extract
2025-10-31
-
Wheat Germ Extract
2025-10-31
-
Beetroot juice Powder
2025-10-31
-
Medicinal Marshmallow Extract
2025-10-31
-
Nutmeg Extract
2025-10-31
-
Ginger Extract
2025-10-31
-
Mangosteen extract powder
2025-10-31





















