- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Side Effects of Green Tea Leaf Extract: What You Need to Know
2025-06-26
Green tea, derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, has gained a reputation as a health-promoting beverage rich in antioxidants and bioactive compounds. Among its various forms, green tea leaf extract is becoming increasingly popular as a dietary supplement due to its concentrated levels of beneficial polyphenols, particularly catechins such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). While recognized for its potential health benefits, it is important to understand that green tea leaf extract, like any supplement, can also pose side effects. This article provides an in-depth examination of the side effects associated with green tea leaf extract, enabling consumers to make informed decisions.
Understanding Green Tea Leaf Extract
Green tea leaf extract is a concentrated form of green tea, typically found in capsules, powders, or liquid supplements. It contains a high concentration of catechins, the most potent of which is EGCG, known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic benefits. The extract is celebrated for promoting weight loss, enhancing brain function, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. However, its high potency also means that users may experience side effects that are less common with the consumption of traditionally brewed green tea.
Potential Side Effects of Green Tea Leaf Extract
1. Caffeine Sensitivity and Related Symptoms
Green tea leaf extract naturally contains caffeine, though generally less than black tea or coffee. Nevertheless, for individuals sensitive to caffeine, even modest amounts can trigger symptoms such as jitteriness, increased heart rate, insomnia, and nervousness. It can also lead to digestive issues, including nausea and upset stomach. Those with caffeine sensitivity should opt for caffeine-free versions of the supplement or consume it in moderation.
2. Liver Toxicity
One of the more serious concerns associated with high doses of green tea leaf extract is liver toxicity. Although rare, there have been cases where high intake has been linked to hepatic injury, manifesting as elevated liver enzymes or more acute liver dysfunction. Symptoms of liver issues include jaundice, abdominal pain, and dark urine. It is crucial for individuals to adhere to recommended dosages and consult healthcare professionals, especially those with pre-existing liver conditions or those taking medications metabolized by the liver.
3. Gastrointestinal Discomfort
Green tea leaf extract can cause gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals. Common symptoms include stomach upset, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. The catechins in green tea, particularly when consumed in high concentrations, can irritate the stomach lining, leading to these issues. To reduce the risk of gastrointestinal upset, it is advisable to take the extract with food.
4. Interference with Nutrient Absorption
The tannins present in green tea leaf extract can interfere with the absorption of certain minerals, such as iron and calcium. This is particularly relevant for individuals who rely on plant-based diets or those with higher iron or calcium needs, such as pregnant women or growing children. It is advisable to separate the consumption of Green Tea Extract from meals rich in these minerals to minimize interference with absorption.
5. Effects on Blood Clotting
The polyphenols in green tea, including EGCG, can influence platelet function and, consequently, blood clotting. This can enhance the effects of anticoagulant or antiplatelet medications, increasing the risk of bleeding. Individuals on blood-thinning medication or those with bleeding disorders should exercise caution and seek medical advice before using green tea leaf extract supplements.
6. Allergic Reactions
Although uncommon, some individuals may experience allergic reactions to green tea leaf extract. Symptoms may include skin rashes, itching, or difficulty breathing. If an allergic reaction is suspected, it is essential to discontinue use and seek medical attention.
7. Effects on Hormones and Metabolism
There is some evidence indicating that green tea leaf extract can influence hormone levels and metabolism. For example, it may alter the function of thyroid hormones or affect blood sugar regulation. While these effects can be beneficial in some contexts, such as weight management, they can pose risks for individuals with thyroid disorders or diabetes. It is essential to monitor hormone levels and blood glucose when introducing Green Tea Extract into the diet, particularly for individuals with known metabolic conditions.
Safe Consumption and Recommendations
To minimize the risk of side effects while still benefiting from green tea leaf extract, consider the following recommendations:
- Moderation is Key: Adhere to recommended dosages as specified on product labels or by healthcare professionals. More is not necessarily better when it comes to supplements.
- Consult Healthcare Providers: Before starting any new supplement, consult with a healthcare provider, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
- Choose Reputable Brands: Select high-quality supplements from reputable brands that provide third-party testing or verification of their products' purity and potency.
- Monitor for Side Effects: Be attentive to any unusual symptoms or side effects, and discontinue use if they occur. Keep an open line of communication with healthcare providers about any changes in your health when taking supplements.
- Consider Caffeine Content: If sensitive to caffeine, seek caffeine-free options or adjust the timing of consumption to avoid sleep disturbances or anxiety.
Conclusion
Green tea leaf extract offers a powerful way to harness the health benefits of green tea, but it also demands respect for its potential side effects. While most individuals can enjoy its advantages with minimal risk, being mindful of caffeine content, dosage, and individual health needs is crucial. With careful consideration and informed use, green tea leaf extract can be a valuable addition to a health-conscious lifestyle, contributing to overall wellness while safeguarding against adverse effects.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Sophora Flavescens Root Extract
2025-06-26
-
Stevia Extract
2025-06-26
-
Epimedium extract powder
2025-06-26
-
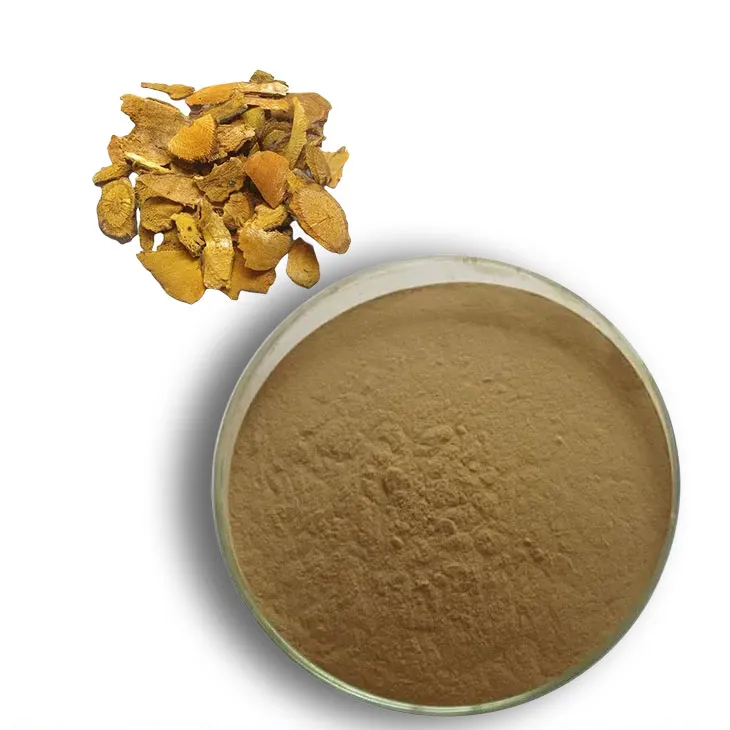
Curcuma Longa Extract/Turmeric extract
2025-06-26
-
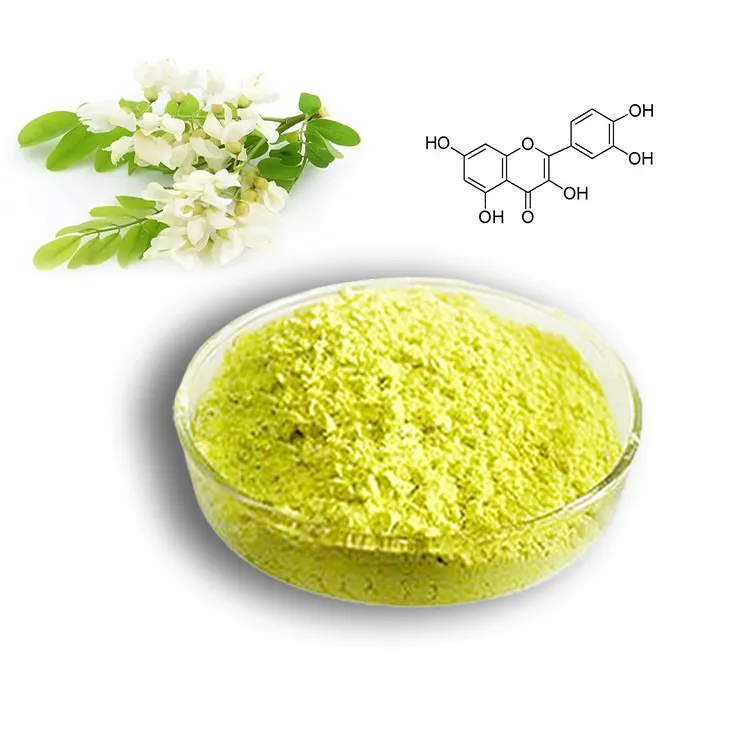
Quercetin
2025-06-26
-
Astaxanthin
2025-06-26
-
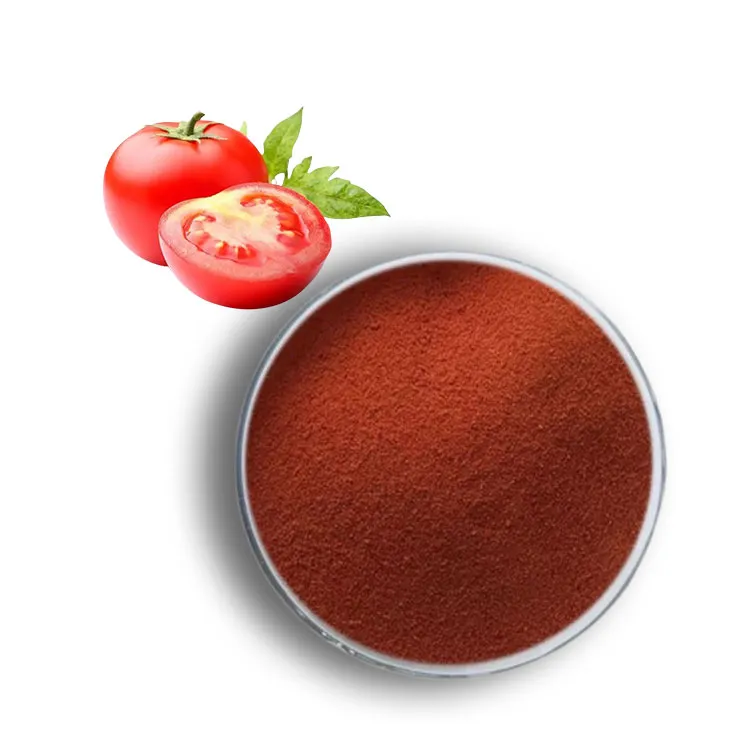
Lycopene
2025-06-26
-
Polygonum Cuspidatum Extract
2025-06-26
-
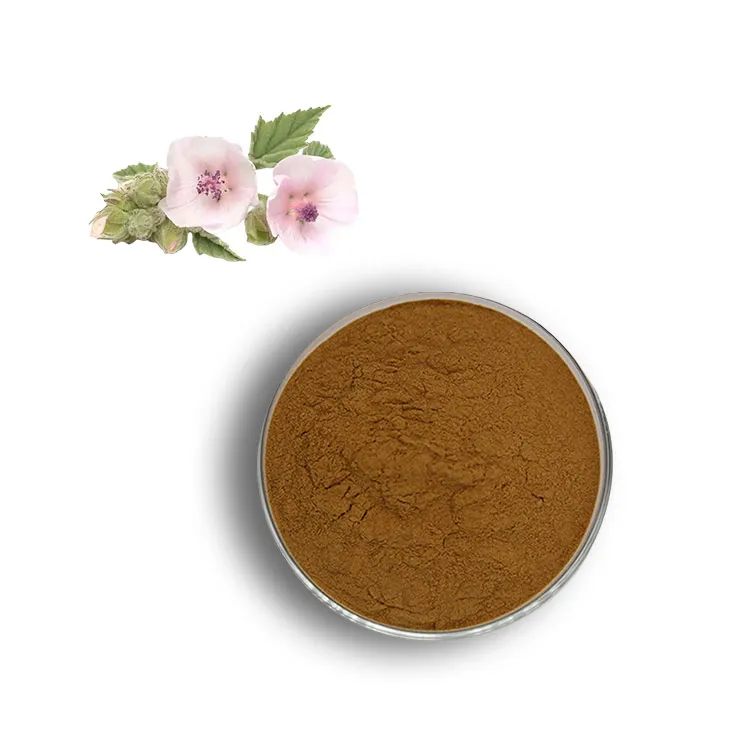
Medicinal Marshmallow Extract
2025-06-26
-
Konjac Powder
2025-06-26