- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Astaxanthin: Discovery, History, and its Role in Health
2025-10-31
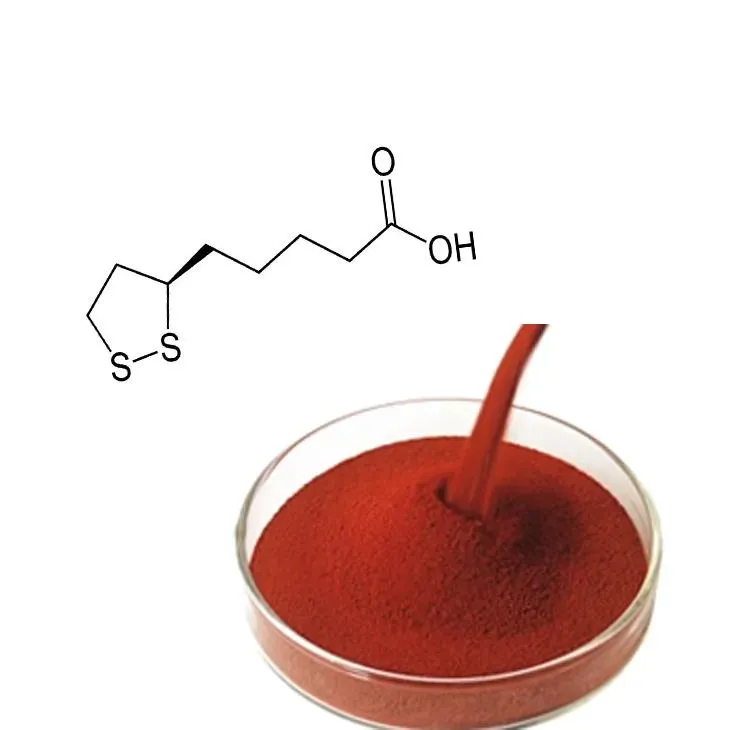
Astaxanthin, a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment, is celebrated for its vibrant red color and potent antioxidant properties. Found in various marine organisms, including microalgae, salmon, krill, and shrimp, Astaxanthin has garnered significant interest over the years for its broad-spectrum health benefits. However, its discovery and subsequent journey to becoming a sought-after nutraceutical are less frequently discussed. This article delves into the history of Astaxanthin, tracing its discovery, development, and its prominent role in health and nutrition today.
The Discovery of Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin was first isolated in 1938 by German scientists Richard Kuhn and Paul A. Karrer. These pioneering chemists were instrumental in the field of carotenoid research, elucidating the structure and properties of these vital pigments. Kuhn and Karrer isolated astaxanthin from the lobster species Astacus gammarus, which is why it was given the name astaxanthin. This discovery followed their extensive work on carotenoids, which are naturally occurring pigments responsible for the red, orange, and yellow colors in many plants and animals.
Kuhn and Karrer’s exploration of carotenoids was motivated by a broader scientific interest in understanding plant coloration and its biological significance. Their work on carotenoids, including astaxanthin, laid the groundwork for later studies into the biological roles and health benefits of these compounds. Notably, both Kuhn and Karrer received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1938 for their extensive research on carotenoids and vitamins, underscoring the impact of their discoveries.
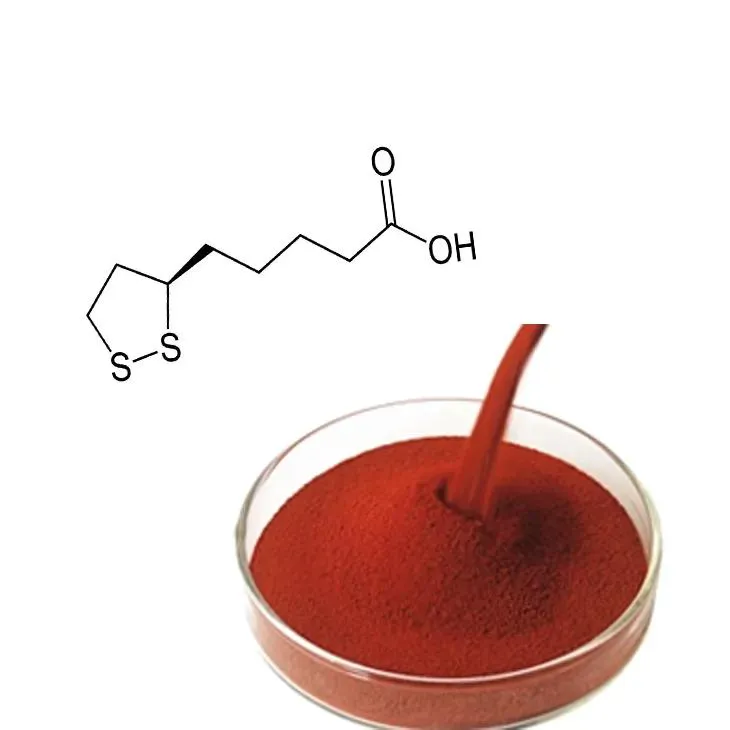
Astaxanthin's Unique Properties
Astaxanthin is distinguished from other carotenoids by its unique molecular structure, which endows it with powerful antioxidant capabilities. Unlike other antioxidants, astaxanthin has the ability to quench free radicals and mitigate oxidative stress without converting into a pro-oxidant form. This makes it exceptionally effective at protecting cells from damage. Additionally, astaxanthin has a unique chemical configuration that allows it to span cellular membranes, providing comprehensive protection at a cellular level.
These attributes have propelled astaxanthin to the forefront of research into natural molecules that combat oxidative stress, inflammation, and aging. Its potent antioxidant properties are considered 6,000 times stronger than vitamin C and up to 500 times more potent than vitamin E, placing it among the most powerful antioxidants known.

The Development of Astaxanthin as a Health Supplement
After its initial discovery, astaxanthin remained relatively obscure in the scientific community until the latter half of the 20th century. The growing interest in natural antioxidants and their roles in health promotion led to increased research into astaxanthin's benefits. As scientific understanding of oxidative stress, inflammation, and their links to chronic diseases expanded, so too did the exploration of astaxanthin’s potential applications.
In the 1980s and 1990s, research into astaxanthin began to accelerate, particularly its health implications for humans and animals. Studies investigated its benefits in various areas, including eye health, skin protection, cardiovascular support, and immune system enhancement. This research prompted the development of astaxanthin as a dietary supplement, available in various forms such as capsules, tablets, and soft gels.
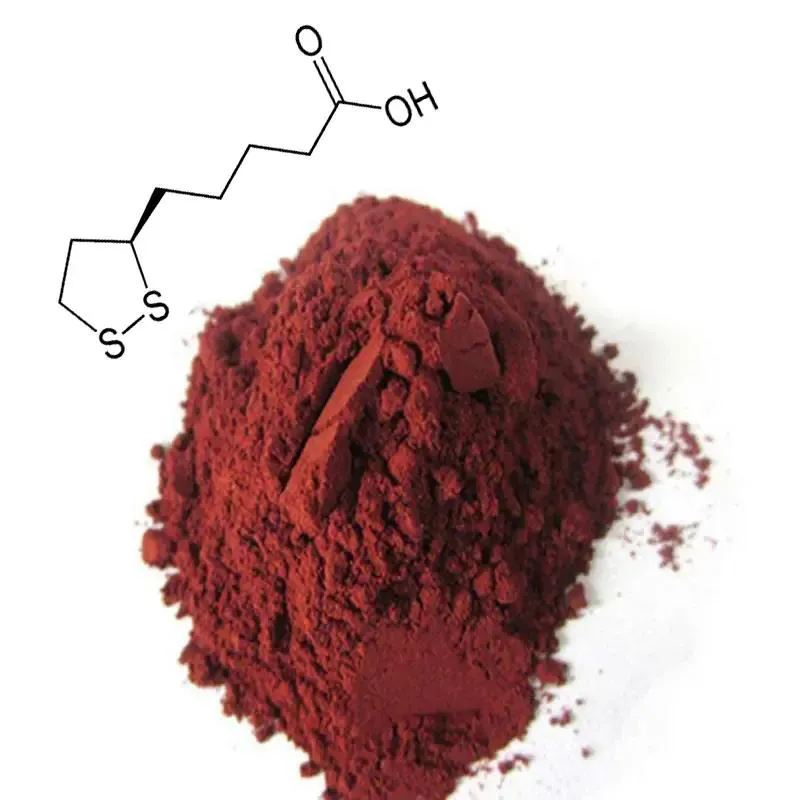
Natural vs. Synthetic Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is derived from both natural and synthetic sources. Naturally sourced astaxanthin is primarily extracted from the microalga Haematococcus pluvialis, which produces high concentrations of the pigment. Krill and crustacean extracts also supply natural astaxanthin. Synthetic astaxanthin, on the other hand, is produced through chemical synthesis and is often utilized in aquaculture to enhance the pigmentation of farmed salmon.
While synthetic astaxanthin provides a cost-effective solution for industrial uses, natural astaxanthin is generally preferred for human health applications. Research suggests that natural astaxanthin sources may possess superior bioavailability and antioxidant efficacy compared to their synthetic counterparts. This has led to a preference for natural astaxanthin in the nutraceutical market.
Astaxanthin in Modern Health and Wellness
Today, astaxanthin is promoted for a variety of health benefits. Its antioxidant potency is central to its role in preventing oxidative stress and reducing inflammation, factors implicated in numerous chronic diseases and aging processes. Here are a few areas where astaxanthin’s effects are particularly noted:
Eye Health
Astaxanthin is celebrated for its potential benefits in maintaining eye health and preventing age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Its antioxidant properties help protect retinal cells from oxidative damage and support overall ocular health.
Skin Protection
Due to its ability to mitigate oxidative stress, astaxanthin is used in skincare formulations to protect against UV-induced skin damage, improve skin elasticity, and reduce the appearance of wrinkles. Its inclusion in topical applications provides a natural method of skin protection and rejuvenation.
Cardiovascular Health
Astaxanthin’s anti-inflammatory effects may contribute to cardiovascular health by improving blood lipid profiles and reducing blood pressure. Some studies have indicated that astaxanthin supplementation can enhance blood flow and reduce markers associated with heart disease, making it a potential ally in heart health management.
Exercise Recovery and Performance
Astaxanthin is gaining popularity among athletes and fitness enthusiasts for its potential to improve endurance and reduce exercise-induced oxidative stress. Its anti-inflammatory benefits may aid in reducing muscle soreness and fatigue, facilitating faster recovery post-exercise.
Immune System Support
Emerging research suggests that astaxanthin can modulate immune responses, potentially enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections and inflammatory conditions. This makes it a valuable supplement for overall immune support.
Future Directions and Research
The exploration of astaxanthin’s health benefits is an evolving field, with ongoing research aimed at uncovering new applications and understanding its mechanisms of action. Future studies may further elucidate its role in neurological health, metabolic disorders, and cancer prevention, solidifying its status as a critical component in health and wellness strategies.
Conclusion
Since its discovery in 1938, astaxanthin has emerged as a leading natural compound with extensive applications in health and wellness. Its remarkable antioxidant properties and diverse health benefits make it a valuable addition to diets and skincare regimens worldwide. As research continues to expand, the potential of astaxanthin to contribute to improved quality of life and the prevention of chronic diseases becomes increasingly apparent. Its journey from a laboratory discovery to a staple in contemporary nutraceuticals underscores the importance of scientific exploration in uncovering nature's treasures for promoting human health.
Visit Greenskybio.com, a great article source where you can learn about Supplements and their health benefits, you also can get the latest food Supplements. Green Sky Bio provides the best extracts and supplements. It is a Chinese self-developed brand that is trustworthy! Welcome to email us to inquire about our products.
TAGS:- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Red Date Extract
2025-10-31
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2025-10-31
-
Chia Seed Powder
2025-10-31
-
Diosmin
2025-10-31
-
Medicinal Marshmallow Extract
2025-10-31
-
Motherwort Extract
2025-10-31
-
Thunder God Vine Extract
2025-10-31
-
Hawthorn Extract
2025-10-31
-
Red Vine Extract
2025-10-31
-
Soy Extract
2025-10-31