- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
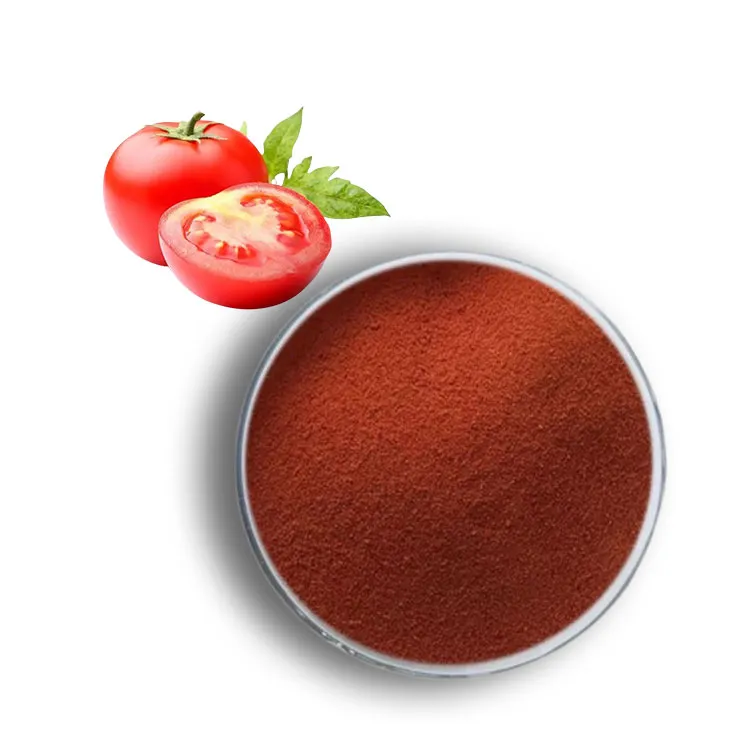
is lycopene good for you
2023-09-27

1. What is Lycopene?
1. What is Lycopene?
Lycopene is a powerful natural pigment and a potent antioxidant belonging to the carotenoid family, which is responsible for the vibrant red color found in various fruits and vegetables. It is structurally similar to other carotenoids such as beta-carotene and lutein but is unique in its ability to absorb and neutralize free radicals in the body. Lycopene is known for its high concentration in tomatoes and tomato-based products, but it can also be found in other red-hued foods like watermelon, pink grapefruit, and red bell peppers.
This nutrient is fat-soluble, meaning it dissolves in fats and oils rather than in water, and is best absorbed when consumed with a small amount of dietary fat. Lycopene's antioxidant properties have been extensively studied for their potential health benefits, including its role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, promoting cardiovascular health, and supporting skin health. Its ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce inflammation makes it a valuable component of a balanced diet for overall wellness.
2. Sources of Lycopene in Diet
2. Sources of Lycopene in Diet
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that is naturally found in a variety of fruits and vegetables. It is particularly abundant in red-colored produce, which is where it gets its vibrant hue. Here are some of the primary dietary sources of lycopene:
1. Tomatoes and Tomato Products: Tomatoes are perhaps the most well-known source of lycopene. This carotenoid is what gives tomatoes their red color. Tomato sauce, paste, and ketchup are also rich in lycopene, especially when cooked, as the heat helps to release it from the plant's cell walls.
2. Watermelon: Another red fruit that contains lycopene is watermelon. It is a refreshing source of this nutrient, particularly during the summer months.
3. Grapes: Red grapes, especially those used to make red wine, are a good source of lycopene. The skin of the grape contains the most lycopene, so consuming whole grapes or drinking red wine can be beneficial.
4. Papaya: This tropical fruit is not only delicious but also a good source of lycopene. It is particularly high in this nutrient when it is ripe and red.
5. Guerita: Also known as tree tomato or tamarillo, this fruit is native to the Andes and is another good source of lycopene.
6. Pink Grapefruit: While not as high in lycopene as some other fruits, pink grapefruit does contain a modest amount of this nutrient.
7. Red Bell Peppers: Although not as rich in lycopene as tomatoes, red bell peppers still offer a good amount of this carotenoid.
8. Pomegranate: This fruit is known for its numerous health benefits, and it also contains lycopene.
9. Cranberries: While not as high in lycopene as some other fruits, cranberries do contain a small amount of this nutrient.
10. Apricots: Dried apricots can be a good source of lycopene, especially when consumed in moderate amounts.
11. Carrots: Carrots are known for their beta-carotene content, but they also contain small amounts of lycopene.
12. Pumpkin: Similar to carrots, pumpkins contain a variety of carotenoids, including lycopene.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can help increase your lycopene intake. It's important to note that cooking tomatoes and consuming them with a little fat can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for your body to absorb and utilize this nutrient. Additionally, a varied diet that includes a range of colorful fruits and vegetables can provide a broad spectrum of nutrients, including lycopene, to support overall health.
3. Health Benefits of Lycopene
3. Health Benefits of Lycopene
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant and a carotenoid, which is a pigment found in many red fruits and vegetables. It has gained significant attention in the scientific community for its potential health benefits. Here are some of the key health advantages associated with lycopene:
1. Antioxidant Properties: Lycopene is a potent antioxidant that helps to neutralize free radicals in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and various diseases.
2. Reduced Risk of Heart Disease: As discussed in the section on cardiovascular health, lycopene has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease by improving blood lipid profiles and reducing inflammation.
3. Cancer Prevention: Lycopene's antioxidant properties may help prevent cancer by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, which are factors that can lead to the development of cancer cells.
4. Improved Skin Health: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of lycopene can help protect the skin from environmental damage and may reduce the signs of aging.
5. Enhanced Vision Health: Some studies suggest that lycopene may help protect against age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults.
6. Bone Health: Research indicates that lycopene may play a role in maintaining bone health, potentially reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
7. Prostate Health: Lycopene has been extensively studied for its potential to reduce the risk of prostate cancer, with some studies showing a positive correlation between lycopene intake and reduced prostate cancer risk.
8. Improved Fertility: Some research suggests that lycopene may improve sperm quality and function, which could contribute to better fertility outcomes in men.
9. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic diseases.
10. Immune System Support: Antioxidants like lycopene can support the immune system by protecting cells from damage and supporting overall immune function.
In summary, lycopene is a nutrient with a wide range of health benefits, from supporting cardiovascular health to potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers and improving skin health. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet can be a natural way to boost your intake of this beneficial compound.
4. Lycopene and Cardiovascular Health
4. Lycopene and Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, and lycopene has been the subject of numerous studies due to its potential role in promoting heart health. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect the cardiovascular system in several ways:
4.1 Antioxidant Properties
Lycopene's antioxidant capabilities are vital for cardiovascular health. Oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body's ability to counteract or detoxify their harmful effects, can lead to damage in the heart and blood vessels. Lycopene helps to neutralize these free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and protecting the heart.
4.2 Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a key factor in the development of cardiovascular diseases. Lycopene has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the body, including in the cardiovascular system. This can be particularly beneficial in preventing the onset of conditions such as atherosclerosis, where inflammation plays a significant role.
4.3 Lowering Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Some research indicates that lycopene may help lower blood pressure, which in turn can reduce the risk of these cardiovascular events.
4.4 Improving Cholesterol Levels
Lycopene may also contribute to improving cholesterol levels, specifically by increasing the levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or "good" cholesterol, while decreasing the levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or "bad" cholesterol. This balance is crucial for maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
4.5 Blood Vessel Health
Healthy blood vessels are essential for efficient blood flow and oxygen delivery throughout the body. Lycopene has been found to improve the elasticity and function of blood vessels, which can help prevent the hardening of the arteries—a condition known as arteriosclerosis.
4.6 Clinical Studies and Observations
While the exact mechanisms of how lycopene benefits cardiovascular health are still being explored, numerous clinical studies and observational research have shown a correlation between higher lycopene intake and a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases.
4.7 Recommendations for Intake
To maximize the cardiovascular benefits of lycopene, it is recommended to incorporate a variety of lycopene-rich foods into your diet. Additionally, cooking these foods with a small amount of healthy fats can enhance the bioavailability of lycopene, making it more readily absorbed by the body.
In conclusion, while more research is needed to fully understand the extent of lycopene's impact on cardiovascular health, the current evidence suggests that it plays a significant role in maintaining a healthy heart and circulatory system. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet can be a beneficial strategy for heart health.
5. Lycopene and Cancer Prevention
5. Lycopene and Cancer Prevention
Lycopene has been the subject of numerous scientific studies due to its potential role in cancer prevention. This powerful antioxidant is believed to play a significant part in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancers.
Mechanisms of Action:
- Antioxidant Properties: Lycopene's antioxidant capabilities help neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and lead to cancer.
- DNA Protection: It has been shown to protect DNA from oxidative damage, which is a critical step in the development of cancer.
- Cell Cycle Regulation: Lycopene can influence the cell cycle, preventing abnormal cell growth that can lead to cancer.
- Apoptosis Induction: It may induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in cancer cells without affecting healthy cells.
Prostate Cancer:
- Several studies have indicated a link between high lycopene intake and a reduced risk of prostate cancer. The Health Professionals Follow-up Study, for example, found that men with the highest intakes of lycopene had a lower risk of advanced prostate cancer.
Lung Cancer:
- Research has suggested that individuals with higher blood levels of lycopene may have a decreased risk of lung cancer, especially in current and former smokers.
Stomach Cancer:
- Lycopene's antioxidant properties may help protect the stomach lining from oxidative stress, potentially reducing the risk of stomach cancer.
Other Cancers:
- While more research is needed, some studies have also hinted at a possible protective effect of lycopene against other types of cancer, such as breast and colorectal cancers.
Dietary Recommendations:
- To maximize the potential cancer-preventive effects of lycopene, it is recommended to consume a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in lycopene, such as tomatoes and watermelon.
Supplementation:
- While a diet rich in lycopene is the preferred method of intake, some individuals may consider lycopene supplements as a way to increase their levels. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen.
In conclusion, while more research is necessary to fully understand the extent of lycopene's role in cancer prevention, current evidence suggests that it is a valuable nutrient for maintaining overall health and potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet can be a simple and effective way to boost your intake of this beneficial compound.
6. Lycopene and Skin Health
6. Lycopene and Skin Health
Lycopene's role in skin health is an area of growing interest due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The skin, being the largest organ of the body, is constantly exposed to environmental stressors such as ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pollution, and free radicals, which can lead to premature aging and skin damage.
Antioxidant Protection
Lycopene is a potent antioxidant that can help protect the skin from oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body's ability to neutralize them. Lycopene can help neutralize these harmful molecules, reducing the risk of skin damage and promoting overall skin health.
UV Protection
One of the primary functions of lycopene in skin health is its ability to protect against UV radiation. UV rays can cause DNA damage, leading to skin aging and an increased risk of skin cancer. Lycopene has been shown to absorb UV light, reducing the penetration of harmful rays into the skin and providing a natural form of photoprotection.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a common cause of various skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation in the skin, alleviating symptoms and promoting a healthier complexion.
Collagen Synthesis
Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin. Lycopene has been shown to stimulate collagen synthesis, which can help maintain skin firmness and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Skin Cancer Prevention
While more research is needed, some studies suggest that lycopene may have a protective effect against skin cancer. Its antioxidant properties can help neutralize free radicals that can damage skin cells and lead to the development of cancerous cells.
Topical Applications
In addition to dietary intake, lycopene can also be applied topically to the skin in the form of creams and serums. Topical application of lycopene can provide direct antioxidant protection to the skin, helping to reduce the signs of aging and protect against environmental stressors.
In conclusion, lycopene's potential benefits for skin health are promising. By incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet and considering topical applications, you may be able to improve your skin's appearance and protect it from environmental damage. However, it's essential to remember that a balanced diet, proper skincare routine, and sun protection are still crucial for maintaining healthy skin.
7. Lycopene and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
7. Lycopene and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Lycopene is not only a potent antioxidant, but it also possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can contribute to overall health and well-being. Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to a variety of health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Mechanism of Action
The anti-inflammatory effects of lycopene are thought to be due to its ability to modulate the activity of various inflammatory pathways. It has been shown to reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that play a key role in the inflammatory response. By doing so, lycopene can help to suppress inflammation and promote a more balanced immune response.
Benefits for Chronic Conditions
Chronic inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma can benefit from the anti-inflammatory properties of lycopene. While more research is needed to fully understand the extent of these benefits, early studies suggest that a diet rich in lycopene may help to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms associated with these conditions.
Skin Health and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
In addition to its internal benefits, lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties can also be beneficial for skin health. Inflammation is a common factor in many skin conditions, including acne, eczema, and psoriasis. By reducing inflammation, lycopene may help to improve the appearance and health of the skin.
Foods Rich in Lycopene and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
To take advantage of lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties, it's important to include lycopene-rich foods in your diet. Some of the best sources of lycopene, as mentioned earlier, include tomatoes, watermelon, pink grapefruit, and guava. These foods not only provide the benefits of lycopene but also contain other nutrients and antioxidants that can support a healthy inflammatory response.
Conclusion
While more research is needed to fully understand the extent of lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties, early evidence suggests that it can play a role in reducing inflammation and promoting overall health. By incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet, you can potentially reduce the risk of chronic inflammatory conditions and support healthy skin. As always, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen.
8. How to Increase Lycopene Intake
8. How to Increase Lycopene Intake
To maximize the health benefits of lycopene, it's essential to incorporate more lycopene-rich foods into your diet. Here are some practical ways to increase your lycopene intake:
1. Eat More Tomatoes: As the primary source of lycopene, tomatoes can be consumed in various forms, including fresh, cooked, or in processed products like tomato sauce, paste, and ketchup.
2. Cooked Tomatoes: Cooking tomatoes, especially with a bit of fat, can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for your body to absorb.
3. Tomato Products: Canned tomatoes, tomato juice, and tomato soup are convenient ways to increase lycopene intake. Look for products with no added sugars or artificial ingredients.
4. Red-Colored Fruits and Vegetables: In addition to tomatoes, other red-colored fruits and vegetables like watermelon, red grapefruit, and red bell peppers are good sources of lycopene.
5. Cook with Tomato Sauce: Use tomato sauce as a base for pasta dishes, stews, or soups to add flavor and lycopene to your meals.
6. Add to Salads: Incorporate cherry tomatoes, watermelon, or red bell peppers into your salads for a colorful and nutritious boost.
7. Consume Lycopene-Rich Juices: Some juices, particularly those made from tomatoes or watermelon, can be a good source of lycopene.
8. Pair with Healthy Fats: Combine lycopene-rich foods with sources of healthy fats, such as olive oil, avocado, or nuts, to enhance absorption.
9. Diversify Your Diet: Include a variety of lycopene-containing foods to ensure you're getting a broad range of nutrients.
10. Supplements: If you're unable to get enough lycopene through diet alone, consider taking a lycopene supplement after consulting with a healthcare provider.
Remember, while increasing lycopene intake is beneficial, it's also important to maintain a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle for overall well-being.
9. Conclusion and Recommendations
9. Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, lycopene is a powerful antioxidant and carotenoid that offers a multitude of health benefits. From its role in cardiovascular health to its potential in cancer prevention and skin protection, lycopene is an essential nutrient that should not be overlooked in a balanced diet.
To maximize the health benefits of lycopene, it is recommended to incorporate a variety of lycopene-rich foods into your daily meals. This includes tomatoes and tomato-based products, watermelon, pink grapefruit, guava, and red bell peppers. Cooking these foods can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for your body to absorb and utilize this nutrient.
In addition to dietary sources, supplementation may be considered for individuals who have difficulty obtaining adequate amounts of lycopene through food alone. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Lastly, maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can further enhance the benefits of lycopene and contribute to overall well-being.
In summary, lycopene is a valuable nutrient with numerous health-promoting properties. By incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet and considering supplementation when necessary, you can support your body's natural defenses and promote a healthier, more vibrant life.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Mango flavored powder
2023-09-27
-
Marigold Extract
2023-09-27
-
Apricot Powder
2023-09-27
-
Thunder God Vine Extract
2023-09-27
-
Buckthorn bark extract
2023-09-27
-
Phyllanthus Emblica Extract
2023-09-27
-
Citrus bioflavonoids
2023-09-27
-
Resveratrol extract
2023-09-27
-
Rosemary extract
2023-09-27
-
Curcuma Longa Extract
2023-09-27