- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
What Is the Ingredient in Horse Chestnut?
2025-10-30
Horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum) is a tree native to parts of Europe, widely known for its glossy leaves, large flowers, and spiky fruit. Beyond its ornamental value, horse chestnut has a long history of medicinal use. The seeds, leaves, bark, and flowers of the horse chestnut tree are used in herbal medicine, particularly for treating circulatory issues.
Understanding the key ingredient in horse chestnut is essential for anyone seeking to benefit from its therapeutic properties. This article explores the chemical composition of horse chestnut, its primary bioactive compounds, health benefits, safety considerations, and how it is used today.
What Are the Main Ingredients in Horse Chestnut?
What Is Aescin?
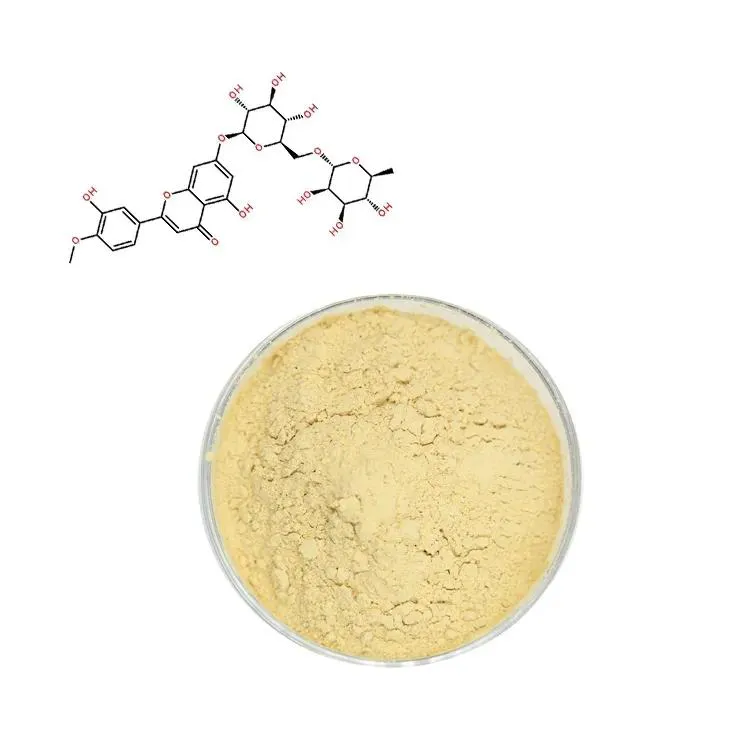
The primary active ingredient in horse chestnut is aescin, also called escin, a mixture of saponins. Saponins are naturally occurring compounds found in many plants that have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and vascular-protective properties.
Aescin is concentrated mainly in the seeds of the horse chestnut tree, although smaller amounts are found in the bark and leaves. Its chemical structure allows it to strengthen blood vessel walls, reduce swelling, and improve circulation.
Are There Other Important Compounds?
In addition to aescin, horse chestnut contains several other bioactive compounds that contribute to its medicinal effects:
Flavonoids: Antioxidants that protect cells from oxidative stress
Coumarins (e.g., fraxin): Anti-inflammatory and vascular-supportive effects
Tannins: Mild astringent properties, which can help tighten tissues
Polyphenols: General antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects
While aescin is the main therapeutic compound, these additional ingredients can synergistically enhance horse chestnut’s overall health benefits.
How Does Aescin Work in the Body?
How Does Horse Chestnut Affect Blood Vessels?
Aescin primarily works by strengthening capillary walls and improving vein tone. This makes horse chestnut especially useful for conditions involving poor circulation, such as:
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI)
Varicose veins
Swelling in the legs or ankles
Aescin reduces capillary permeability, which prevents fluid from leaking into surrounding tissues. It also has mild anti-inflammatory effects, helping reduce swelling and discomfort associated with vascular problems.
Does Horse Chestnut Have Anti-Inflammatory Effects?
Yes. Studies indicate that aescin can inhibit certain inflammatory enzymes, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This anti-inflammatory activity contributes to relief in conditions like leg edema, hemorrhoids, and minor bruising.
Moreover, flavonoids and polyphenols in horse chestnut complement aescin’s action by scavenging free radicals, reducing oxidative stress in blood vessels.
What Forms of Horse Chestnut Contain the Active Ingredient?
Which Part of the Plant Is Most Potent?
Seeds: The seeds contain the highest concentration of aescin and are the main source for most standardized extracts.
Leaves and Bark: Contain smaller amounts of aescin and other compounds, used occasionally in herbal teas or topical applications.
Flowers: Less commonly used, but contain flavonoids that support antioxidant activity.
What Is a Standardized Horse Chestnut Extract?
For medicinal use, horse chestnut is often prepared as a standardized extract, which ensures a consistent concentration of aescin (usually 16–20%). This standardization is crucial for safety and efficacy, as raw seeds contain substances like esculin, which can be toxic if not properly processed.
What Are the Health Benefits of the Ingredient in Horse Chestnut?
How Does Aescin Support Circulation?
One of the most well-known applications of Horse Chestnut Extract is chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). CVI occurs when veins in the legs cannot pump blood efficiently, leading to swelling, fatigue, and varicose veins. Clinical studies have shown that standardized Horse Chestnut Extract can:
Reduce leg swelling and edema
Improve pain, heaviness, and itching associated with varicose veins
Enhance overall vein tone and elasticity
This makes aescin a natural alternative or complementary therapy to compression stockings and other conventional treatments.
Can Horse Chestnut Reduce Inflammation and Swelling?
Yes. Aescin’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it useful for reducing:
Postoperative swelling
Sports-related bruising
Minor inflammatory conditions
Topical formulations containing horse chestnut extract are sometimes applied to bruises, sprains, and hemorrhoids for localized relief.
Are There Other Potential Benefits?
Emerging research suggests that horse chestnut may also support:
Heart health: By improving blood circulation and reducing edema, it can help with mild cardiovascular support.
Antioxidant protection: Flavonoids and polyphenols may protect blood vessels from oxidative damage.
Skin health: Some creams containing horse chestnut extract may improve skin tone and reduce puffiness due to enhanced microcirculation.
However, more research is needed to confirm these secondary benefits.
Is Horse Chestnut Safe for Humans?
Can Raw Horse Chestnut Be Toxic?
Yes. Raw horse chestnut seeds, bark, and leaves contain esculin, a toxic compound that can cause:
Nausea and vomiting
Dizziness
Muscle twitching
In severe cases, paralysis or death
This is why commercial extracts are carefully processed to remove esculin and other harmful substances. Only standardized extracts or properly prepared seeds should be used for human consumption.
Are There Side Effects From Standardized Extracts?
When taken in recommended doses (usually 300 mg/day of standardized aescin extract), side effects are generally mild and may include:
Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, diarrhea)
Headache
Dizziness
Skin rash (rare)
Most studies indicate that horse chestnut is well-tolerated, with adverse effects being uncommon.
Who Should Avoid Horse Chestnut?
Certain groups should exercise caution:
Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Safety has not been established.
People with bleeding disorders or on anticoagulants: Horse chestnut may increase the risk of bleeding.
Individuals allergic to Aesculus species: Could experience skin or systemic allergic reactions.
Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended before starting supplementation, especially for long-term use or if other medications are taken.
How Is Horse Chestnut Used in Modern Medicine?
What Are Common Dosage Forms?
Horse chestnut extract is available in several forms:
Capsules or tablets: Standardized to 16–20% aescin, for chronic venous insufficiency and leg swelling.
Topical creams and gels: For bruising, swelling, and hemorrhoids.
Teas and tinctures: Less common due to variable aescin content.
How Effective Is Horse Chestnut Compared to Conventional Medicine?
Clinical studies suggest that standardized horse chestnut extract can be as effective as compression therapy for mild to moderate chronic venous insufficiency. Its advantages include being non-invasive and having fewer side effects compared to pharmaceutical treatments.
However, it is generally recommended as a complementary therapy, not a complete replacement for medical treatment in severe cases.
What Should You Look for When Choosing Horse Chestnut Supplements?
How to Ensure Safety and Potency
Check for standardized aescin content: 16–20% is considered therapeutic.
Avoid raw seeds: Only use processed or standardized extracts.
Choose reputable brands: Third-party testing ensures purity and safety.
Follow recommended dosages: Excessive use can increase the risk of side effects.
Are There Quality Certifications to Consider?
Look for:
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certification
USP (United States Pharmacopeia) verified supplements
Organic labeling to reduce pesticide contamination
These certifications help ensure that the product is safe, potent, and free from contaminants.
The Bottom Line: What Is the Key Ingredient in Horse Chestnut and Its Benefits?
The primary ingredient in horse chestnut is aescin, a saponin responsible for its anti-inflammatory, vascular-protective, and antioxidant effects. Horse chestnut extract is widely used to improve circulation, reduce leg swelling, and treat chronic venous insufficiency, with supporting evidence from multiple clinical trials.
Other bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, coumarins, tannins, and polyphenols, complement aescin’s effects and contribute to the overall therapeutic potential.
When properly processed and standardized, horse chestnut is safe for most adults. However, raw seeds are toxic, and certain individuals — including pregnant women, people with allergies, or those on anticoagulants — should avoid or use it cautiously.
In summary, aescin is the cornerstone of horse chestnut’s medicinal value, making this plant a natural and effective supplement for vascular health and circulatory support.
Visit Greenskybio.com, a great article source where you can learn about Supplements and their health benefits, you also can get the latest food Supplements. Green Sky Bio provides the best extracts and supplements. It is a Chinese self-developed brand that is trustworthy! Welcome to email us to inquire about our products.
TAGS:- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
White mustard seed extract
2025-10-30
-
Europen Bilberry Extract
2025-10-30
-
Diosmin
2025-10-30
-
Withania Somnifera Extract
2025-10-30
-
Marigold Extract
2025-10-30
-
Natural grape seed extract
2025-10-30
-
Cranberry Extract
2025-10-30
-
Green coffee bean Extract
2025-10-30
-
Sea buckthorn oil
2025-10-30
-
Nettle leaf extract
2025-10-30