- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Citrus Bioflavonoids: Recommended Daily Intake and Health Benefits
2025-06-20
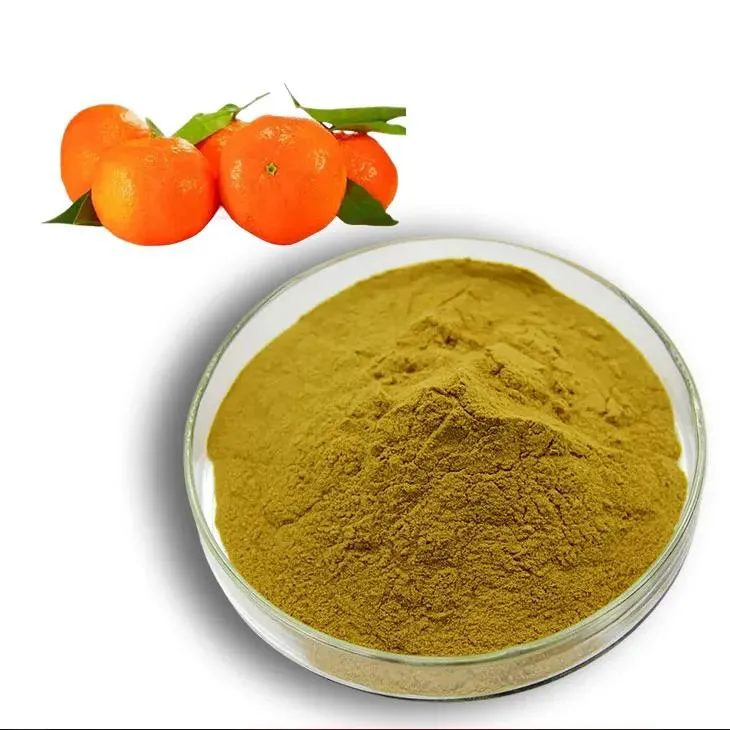

Citrus fruits have long been celebrated for their refreshing flavors and high vitamin C content, but they also contain other important compounds that contribute to their health benefits. Among these are citrus bioflavonoids, a group of polyphenolic compounds with potent antioxidant properties. Understanding the ideal daily intake of citrus bioflavonoids and their potential health benefits is essential for anyone looking to harness their therapeutic potential. This article delves into guidance on how much citrus bioflavonoids should be consumed daily, alongside their benefits, mechanisms of action, and safety considerations.
What Are Citrus Bioflavonoids?
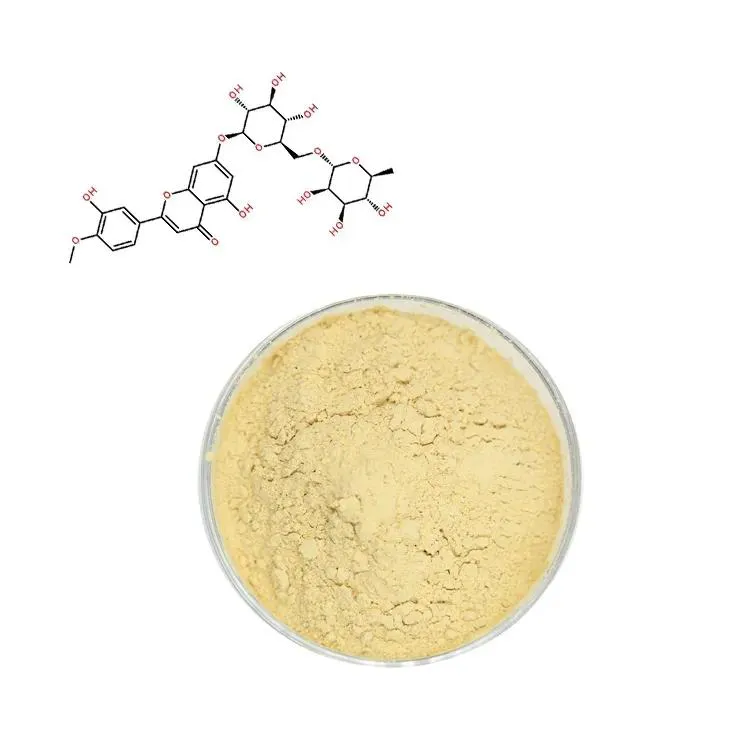
Citrus bioflavonoids are a class of phytonutrients prevalent in citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits. Key bioflavonoids found in these fruits include Hesperidin, naringin, Quercetin, and rutin. These compounds are renowned for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vascular-protective properties. They work synergistically with vitamin C, enhancing its absorption and efficacy, which can lead to improved health outcomes.

Health Benefits of Citrus Bioflavonoids
Citrus bioflavonoids offer a range of health benefits:
1. Antioxidant Activity: Citrus bioflavonoids are excellent antioxidants that neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
2. Vascular Health: These compounds contribute to vascular health by improving endothelial function, enhancing circulation, and reducing capillary fragility. Hesperidin, in particular, has been shown to help support blood vessel integrity.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Citrus bioflavonoids mitigate inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This action may have implications for managing conditions such as arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
4. Immune Support: By modulating immune responses and enhancing the activity of immune cells, citrus bioflavonoids play a critical role in supporting the immune system.
5. Improved Metabolic Health: Some studies suggest that citrus bioflavonoids can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve lipid profiles, thereby benefiting individuals with metabolic syndrome.

Determining the Optimal Daily Intake
Determining the ideal daily intake of citrus bioflavonoids can be challenging, as specific dosage recommendations are not universally established. The dosage depends on several factors, including individual health goals, age, dietary habits, and any underlying health conditions.
A general guideline suggests that adults can safely consume 500 mg to 1,000 mg of citrus bioflavonoids per day. This dosage range is often considered effective in providing health benefits without causing adverse effects. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, as they can offer personalized advice based on individual health needs and possible interactions with medications.

Sources of Citrus Bioflavonoids
To achieve the recommended intake, individuals can consume citrus bioflavonoids through both dietary sources and supplements:
1. Dietary Sources: Eating a variety of citrus fruits and juices is a practical way to incorporate bioflavonoids into the diet. Leaning towards whole fruits rather than juices is preferable due to the additional fiber and lower sugar content.
2. Supplements: Citrus bioflavonoid supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and powders. These can provide concentrated doses of specific bioflavonoids such as Hesperidin or Quercetin.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
Citrus bioflavonoids are generally well-tolerated and safe for most individuals when consumed in moderation through diet. However, excessive intake—especially through supplements—may lead to mild gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea or stomach discomfort.
Moreover, some bioflavonoids can interfere with the metabolism of certain drugs, including some blood pressure medications, statins, and anticoagulants. It is, therefore, imperative for individuals taking prescription medications to consult their healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
Current Research and Future Directions
Research into citrus bioflavonoids continues to expand, unveiling new insights into their therapeutic potential. Recent studies focus on their role in combatting age-related diseases, supporting cognitive function, and enhancing skin health. As scientific techniques advance, the ability to isolate and study individual bioflavonoids offers promising avenues for targeted therapies.
Additionally, ongoing research into bioavailability—how well these compounds are absorbed and utilized by the body—could further refine recommendations around dosing and efficacy, ensuring that individuals can maximize their benefits.
Conclusion
Citrus bioflavonoids represent a powerful asset for health and wellness, offering antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and vascular benefits. With a general recommended dosage of 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day, they can be incorporated into the diet through fruits or supplements following professional guidance. As scientific research continues to unfold, citrus bioflavonoids hold immense promise in supporting a wide range of health outcomes, making them a valuable component of a holistic approach to health and nutrition. As always, individuals should consult healthcare professionals to tailor intake to their specific needs and circumstances.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Marigold Extract
2025-06-20
-
Maitake Mushroom Extract
2025-06-20
-
Chaste Berry Extract
2025-06-20
-
Peppermint Extract Powder
2025-06-20
-
Curcuma Longa Extract
2025-06-20
-
Diosmin
2025-06-20
-
Centella Asiatica Extract
2025-06-20
-
Black Pepper Extract
2025-06-20
-
Moringa powder
2025-06-20
-
Agaricus Blazei Extract
2025-06-20