- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Oregano: A Herb of Ancient Joy with Modern Health Benefits
2025-04-09
Oregano, scientifically termed Origanum vulgare, has a storied past that stretches back to ancient Greece, where it was revered as a symbol of joy and happiness. Derived from the Greek words meaning “mountain joy,” oregano was later embraced by the Romans and has since been cultivated worldwide, flourishing in sunny, well-drained climates.
Rich in valuable phytonutrients such as carvacrol, thymol, rosmarinic acid, flavonoids, and terpenes, oregano delivers antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties. These compounds act synergistically to enhance overall health, aiding in the management of conditions like inflammation, oxidative stress, infections, diabetes, and digestive and respiratory issues.
In Mediterranean cuisine, oregano is a pivotal ingredient, elevating dishes like Margherita pizza, Greek salad, pasta sauces, roasted vegetables, and grilled chicken with its robust, earthy taste. This perennial herb from the mint family showcases small green leaves and flowers ranging from white to purple, imbued with a pungent aroma due to its essential oils.
Throughout history, oregano has been recognized not only for its culinary applications but also for its wide-ranging health benefits. The herb’s high level of phytonutrients such as carvacrol, thymol, and rosmarinic acid contribute significantly to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial advantages.
Historical Roots and Cultural Significance:
Oregano was first discovered by ancient Greeks, who prized it for both culinary and medicinal purposes, using it to address a spectrum of health issues, from respiratory ailments to skin conditions. The Romans spread its usage across their empire, and today it thrives in a variety of regions including the Mediterranean, Europe, Asia, and the Americas.
Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits:
The health benefits of oregano are well-documented, backed by its rich composition of phytonutrients. Its anti-inflammatory effects are beneficial for conditions like arthritis, while its antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer. Additionally, oregano’s antimicrobial activity offers a natural remedy against a variety of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, including those resistant to antibiotics. Some studies suggest oregano may also assist in diabetes management by regulating blood sugar levels. It is traditionally used to soothe digestive issues and improve respiratory health due to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
Culinary Uses Across the Globe:
Oregano is woven into the culinary traditions of many cultures, known as “orégano” in Spanish, “origan” in French, and referred to as “za’atar” in the Middle East. It frequently appears in recipes blending its distinctive warm and aromatic flavor with tomatoes, garlic, and olive oil, making it a staple ingredient in Mediterranean and Italian cuisines.
Oregano remains an invaluable herb contributing both to the flavor profile of dishes and to health and wellness. As you incorporate oregano into your meals, remember its legacy of joy and healing, a testament to the power of nature harnessed over centuries.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2025-04-09
-
Konjac Powder
2025-04-09
-
Alfalfa Meal
2025-04-09
-
Stevia Extract
2025-04-09
-
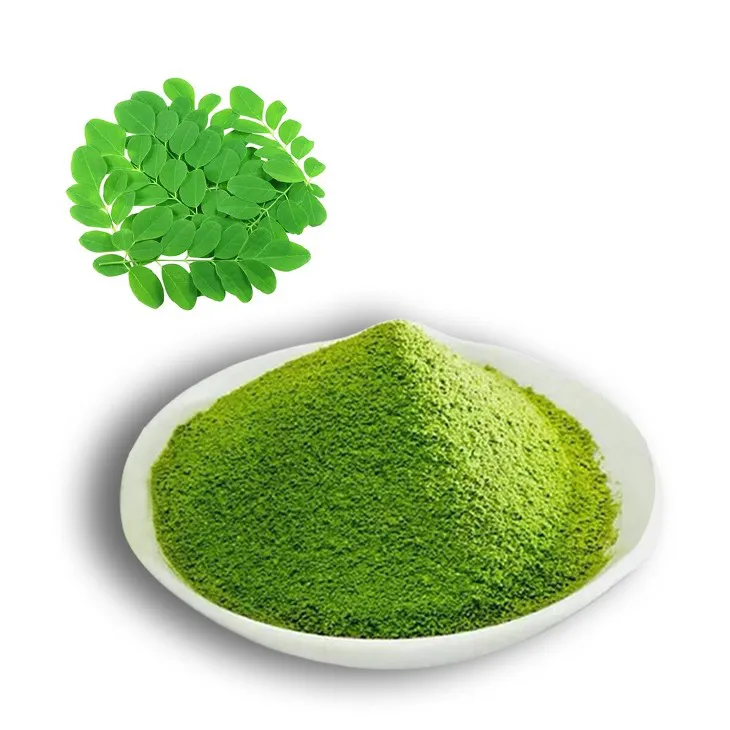
Moringa powder
2025-04-09
-
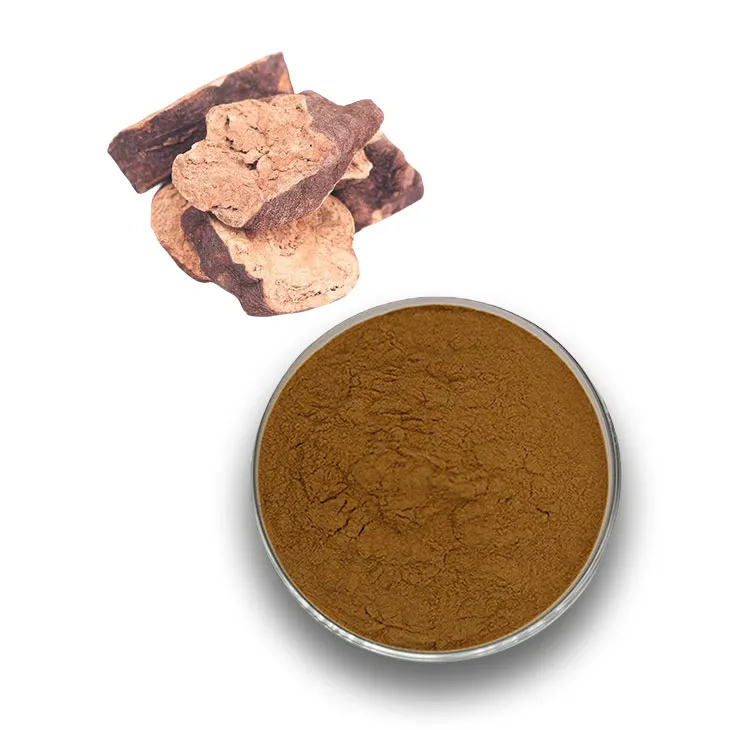
Polygonum multiflorum extract
2025-04-09
-
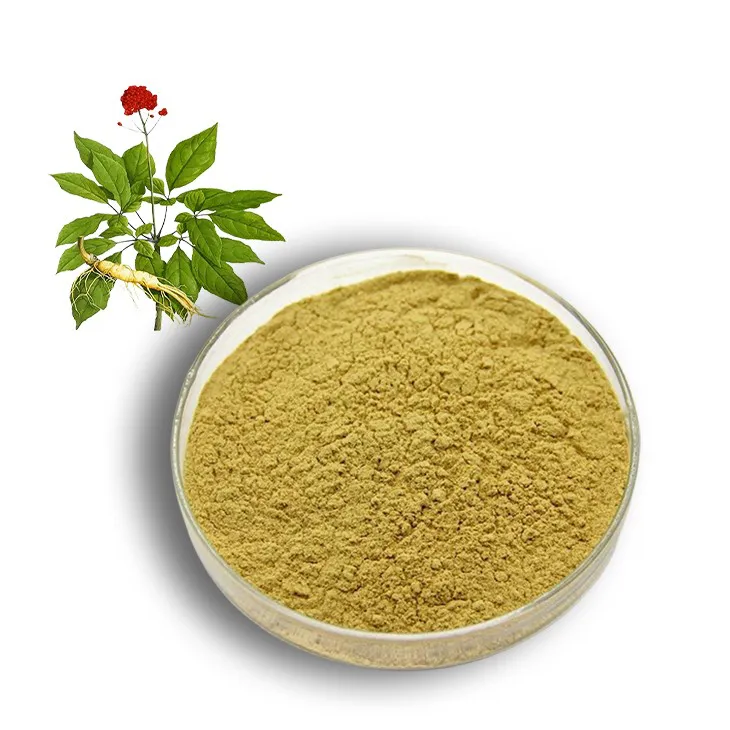
Panax Ginseng Leaf Extract
2025-04-09
-
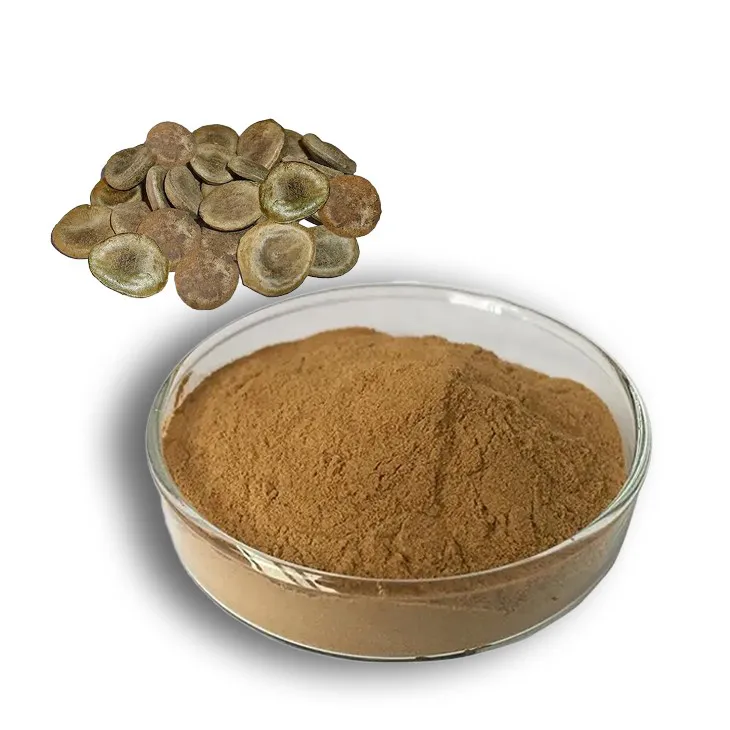
Kupilu Extract
2025-04-09
-
Diosmin
2025-04-09
-
Garcinia Cambogia Extract
2025-04-09