- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
what is lycopene and its benefits
2023-09-28

1. Chemical Structure and Properties of Lycopene
1. Chemical Structure and Properties of Lycopene
Lycopene is a naturally occurring carotenoid, a type of organic pigment that is responsible for the vibrant red color found in many fruits and vegetables. It is synthesized by plants and certain microorganisms, and it plays a crucial role in protecting these organisms from the harmful effects of sunlight. Lycopene is unique among carotenoids due to its structure and properties, which contribute to its health-promoting benefits.
Chemical Structure
The chemical structure of lycopene is characterized by a long chain of carbon-carbon double bonds, with a total of 11 conjugated double bonds. This structure gives lycopene its characteristic red color and makes it one of the most potent carotenoids in terms of antioxidant activity. The conjugated double bonds allow lycopene to absorb light in the visible spectrum, which is why it appears red to the human eye.
Lycopene is a lipophilic compound, meaning it is soluble in fats and oils but not in water. This property is important for its absorption in the human body, as it requires the presence of dietary fats to be efficiently absorbed and transported.
Properties
Some of the key properties of lycopene include:
1. Antioxidant Activity: Lycopene's long chain of conjugated double bonds makes it a powerful antioxidant. It can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and contribute to various diseases.
2. Thermal Stability: Lycopene is relatively stable when exposed to heat, which means that cooking or processing foods containing lycopene does not significantly reduce its levels.
3. Absorption: As a lipophilic compound, lycopene's absorption is enhanced when consumed with dietary fats. This is why it is recommended to consume lycopene-rich foods with some form of fat, such as olive oil or avocado.
4. Bioavailability: The bioavailability of lycopene can be influenced by various factors, including the form in which it is consumed (e.g., raw vs. cooked) and the presence of other nutrients that can either enhance or inhibit its absorption.
5. Aggregation: Lycopene molecules can aggregate, which may affect its bioavailability and biological activity. However, this aggregation can also be beneficial, as it may protect lycopene from degradation during digestion.
Understanding the chemical structure and properties of lycopene is essential for appreciating its role in human health and the ways in which it can be optimally consumed and utilized by the body. As we explore the various health benefits of lycopene in the following sections, we will see how these properties contribute to its effectiveness as a dietary supplement and a natural health-promoting compound.
2. Natural Sources of Lycopene
2. Natural Sources of Lycopene
Lycopene is a naturally occurring carotenoid found in a variety of fruits and vegetables, particularly those with a red color. It is one of the most potent antioxidants in the human diet and is known for its numerous health benefits. Here are some of the primary natural sources of lycopene:
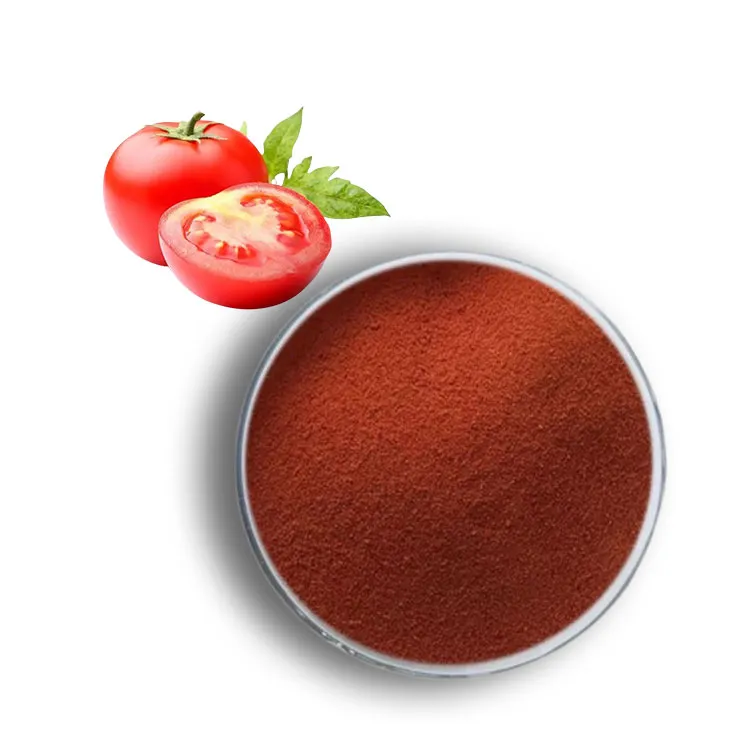
1. Tomatoes and Tomato Products: Tomatoes are the most well-known source of lycopene. The concentration of lycopene in tomatoes can be increased by cooking them, as heat helps to break down the cell walls and release the lycopene. Tomato sauce, paste, and canned tomatoes are particularly high in lycopene.
2. Watermelon: This refreshing fruit is another rich source of lycopene. Its bright red color is a testament to its lycopene content. Watermelon is a great addition to a diet for those looking to increase their lycopene intake.
3. Grapes: Red grapes, especially those used in winemaking, contain significant amounts of lycopene. The skin of the grapes is where most of the lycopene is found, so consuming whole grapes or drinking red wine can be beneficial.
4. Papaya: This tropical fruit is not only delicious but also a good source of lycopene, particularly in its ripe, red form.
5. Guerrero Chili Pepper: Also known as the "Red Savina" pepper, this variety is one of the hottest chili peppers and is high in lycopene content.
6. Pink Grapefruit: While all grapefruits contain lycopene, the pink variety tends to have a higher concentration.
7. Apricots: These small, orange fruits are another source of lycopene, especially when they are more ripe and have a deeper color.
8. Raspberries: Red raspberries contain lycopene, and their antioxidant content can be beneficial for overall health.
9. Red Cabbage: This vegetable is not only a good source of lycopene but also provides a variety of other nutrients.
10. Pomegranate: Known for its powerful antioxidant properties, pomegranate also contains lycopene, particularly in its seeds.
11. Carrot: While carrots are more famous for their beta-carotene content, they also contain small amounts of lycopene.
12. Pumpkin: Similar to carrots, pumpkins contain a variety of carotenoids, including lycopene.
13. Cranberries: These small, red berries are not only tart and flavorful but also contain lycopene.
14. Red Bell Peppers: While not as high in lycopene as some other sources, red bell peppers still contribute to the daily intake.
15. Amaranth Leaves: This leafy green is a good source of lycopene and is often used in salads.
Incorporating these lycopene-rich foods into your diet can be a delicious way to boost your intake of this beneficial nutrient. It's important to note that cooking and processing can sometimes increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for your body to absorb and utilize it.
3. Lycopene's Role in Human Health
3. Lycopene's Role in Human Health
Lycopene is a powerful carotenoid that plays a significant role in human health due to its numerous health-promoting properties. It is a naturally occurring pigment found in various red fruits and vegetables, which is responsible for their vibrant color. The role of lycopene in human health is multifaceted, offering a range of benefits that contribute to overall well-being.
Cardiovascular Health
One of the most notable benefits of lycopene is its positive impact on cardiovascular health. Studies have shown that lycopene can help reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure, improving blood lipid profiles, and reducing inflammation. It also helps to prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, which is a major contributor to atherosclerosis, a condition that can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
Antioxidant Activity
Lycopene's antioxidant properties are crucial in protecting the body from oxidative stress, which can cause cellular damage and contribute to various diseases. As a potent antioxidant, lycopene neutralizes free radicals, preventing them from causing damage to cells and tissues. This protective effect is particularly important for the prevention of chronic diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Skin Health
Lycopene also plays a vital role in maintaining skin health. It has been found to protect the skin from harmful UV radiation, reducing the risk of sunburn and skin cancer. Additionally, lycopene can help slow down the aging process of the skin by reducing wrinkles and improving skin elasticity. This is due to its ability to neutralize free radicals that can cause oxidative damage to the skin.
Cancer Prevention
The cancer-preventive properties of lycopene have been extensively studied. Lycopene has been shown to reduce the risk of various types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancer. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and reduce the risk of tumor development.
Eye Health
Lycopene is also beneficial for eye health. It has been linked to a reduced risk of age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Lycopene's antioxidant properties help protect the delicate tissues of the eye from oxidative damage, preserving vision and promoting eye health.
Prostate Health
One of the most well-known benefits of lycopene is its positive impact on prostate health. Studies have shown that men with higher levels of lycopene in their diet have a lower risk of prostate cancer. Lycopene's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties help to protect the prostate from oxidative stress and inflammation, which can contribute to the development of prostate cancer.
Immune System Support
Lycopene also supports the immune system by enhancing its ability to fight off infections and diseases. Its antioxidant properties help to strengthen the immune system, allowing it to function more effectively and protect the body from harmful pathogens.
Conclusion
In summary, lycopene plays a crucial role in human health, offering a wide range of benefits that contribute to overall well-being. From promoting cardiovascular health to supporting the immune system, the health benefits of lycopene are extensive. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet or considering lycopene supplements can help to ensure that you are receiving the full range of health benefits that this powerful carotenoid has to offer.
4. Antioxidant Properties of Lycopene
4. Antioxidant Properties of Lycopene
Lycopene is a potent antioxidant, which means it can help protect your body against damage from harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and lead to various health problems, including heart disease and cancer.
One of the key antioxidant properties of lycopene is its ability to neutralize free radicals. When free radicals come into contact with lycopene, the antioxidant donates an electron to stabilize the free radical, preventing it from causing damage to cells.
In addition to neutralizing free radicals, lycopene also has other antioxidant properties that can benefit your health. For example, lycopene can help reduce inflammation, which is a common factor in many chronic diseases. It can also help improve blood flow and reduce oxidative stress, which is a major contributor to aging and age-related diseases.
Research has shown that lycopene is one of the most effective antioxidants in terms of its ability to protect cells from damage. In fact, it has been found to be more effective than other well-known antioxidants, such as beta-carotene and vitamin E.
Overall, the antioxidant properties of lycopene make it an important nutrient for maintaining good health and preventing various diseases. By incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet, you can help protect your body against free radical damage and support overall health and wellness.
5. Lycopene and Cardiovascular Health
5. Lycopene and Cardiovascular Health
Lycopene has been extensively studied for its potential role in promoting cardiovascular health. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, and maintaining a healthy heart is crucial for overall well-being. Here's how lycopene contributes to a healthier cardiovascular system:
5.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a significant factor in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, restricting blood flow and increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Lycopene's anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce inflammation in the body, thereby potentially lowering the risk of developing CVDs.
5.2. Blood Pressure Regulation
High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Lycopene has been found to have a positive impact on blood pressure levels. Studies have shown that individuals with higher lycopene intake tend to have lower blood pressure, suggesting that incorporating lycopene-rich foods into the diet can help in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
5.3. Cholesterol Management
High cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease. Lycopene has been shown to help regulate cholesterol levels, particularly by reducing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "bad" cholesterol, while leaving the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, or "good" cholesterol, unaffected.
5.4. Endothelial Function Improvement
The endothelium is the inner lining of blood vessels and plays a critical role in maintaining vascular health. Lycopene has been found to improve endothelial function, promoting better blood flow and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
5.5. Antioxidant Protection for Blood Vessels
As a potent antioxidant, lycopene can protect blood vessels from oxidative stress, which is a key factor in the development of heart disease. By neutralizing free radicals, lycopene helps prevent the damage to blood vessels that can lead to plaque formation and arterial stiffness.
5.6. Clinical Studies and Observations
Several clinical studies and observational research have linked higher lycopene intake with a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. While more research is needed to establish a direct causal relationship, the existing evidence suggests that lycopene can be a valuable component of a heart-healthy diet.
5.7. Recommendations for Cardiovascular Health
To benefit from lycopene's potential cardiovascular health benefits, it is recommended to include a variety of lycopene-rich foods in your diet. These include tomatoes and tomato-based products, watermelon, pink grapefruit, guava, and papaya. Additionally, cooking tomatoes or consuming them with a little fat can enhance lycopene absorption.
In conclusion, lycopene's role in cardiovascular health is multifaceted, with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and cholesterol-regulating properties all contributing to a healthier heart. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet can be a simple yet effective way to support your cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
6. Lycopene's Impact on Skin Health
6. Lycopene's Impact on Skin Health
Lycopene, a potent antioxidant, has been the subject of numerous studies for its potential benefits on skin health. It is believed to play a significant role in protecting the skin from various harmful effects, particularly those caused by environmental factors such as UV radiation and oxidative stress.
Protective Role Against UV Damage
One of the primary benefits of lycopene for skin health is its ability to act as a natural sunscreen. Lycopene absorbs UV light, reducing the amount of harmful radiation that penetrates the skin. This protective effect can help prevent sunburn, premature aging, and the risk of skin cancer.
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Oxidative stress and inflammation are key contributors to skin aging and various skin conditions. Lycopene's antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage skin cells and lead to premature aging signs such as wrinkles and fine lines. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory effects can help alleviate symptoms of skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
Collagen Synthesis
Collagen is a vital protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to sagging and wrinkling. Lycopene has been shown to stimulate collagen synthesis, which can help maintain skin firmness and elasticity, thus contributing to a more youthful appearance.
Skin Hydration
Maintaining skin hydration is crucial for overall skin health and appearance. Lycopene has been found to improve skin hydration by enhancing the skin's ability to retain moisture. This can result in a smoother and more supple complexion.
Anti-Aging Benefits
The combination of lycopene's UV protection, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and collagen-boosting properties contribute to its anti-aging benefits. By protecting the skin from environmental damage and promoting skin health from within, lycopene can help slow down the aging process and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
Topical Application
While dietary intake of lycopene is beneficial for skin health, topical application of lycopene-rich products can also provide direct benefits to the skin. Skincare products containing lycopene can offer protection against UV damage, reduce inflammation, and improve skin hydration and elasticity.
In conclusion, lycopene's impact on skin health is multifaceted, offering protection against UV radiation, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, promoting collagen synthesis, and enhancing skin hydration. Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet or using lycopene-based skincare products can contribute to healthier, more youthful-looking skin.
7. Lycopene and Cancer Prevention
7. Lycopene and Cancer Prevention
Lycopene has been the subject of numerous studies due to its potential role in cancer prevention. The compound's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make it a promising agent in the fight against various types of cancer.
Mechanisms of Action:
Lycopene is believed to exert its cancer-preventive effects through several mechanisms. It can neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells and potentially lead to cancer. By reducing oxidative stress, lycopene may lower the risk of DNA damage and mutations that can trigger cancer development.
Prostate Cancer:
One of the most well-studied areas of lycopene's health benefits is its potential impact on prostate cancer. Several epidemiological studies have suggested that higher intakes of lycopene are associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer. The protective effect of lycopene may be due to its ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (cell death) in prostate cancer cells.
Other Cancers:
While prostate cancer has received the most attention, research also indicates that lycopene may have a positive effect on the prevention of other types of cancer, including lung, stomach, and colorectal cancers. The exact mechanisms may vary, but the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of lycopene are likely contributors.
Dietary Intake vs. Supplementation:
It's important to note that most of the research on lycopene and cancer prevention has been observational, meaning it shows an association but does not prove causation. While dietary intake of lycopene from natural sources is generally considered safe, the effectiveness of lycopene supplements for cancer prevention is still under investigation.
Recommendations:
To potentially benefit from lycopene's cancer-preventive properties, it is recommended to consume a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in lycopene. Foods like tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit are excellent sources. While supplements may be an option for some individuals, it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
In conclusion, while more research is needed to fully understand the extent of lycopene's role in cancer prevention, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties make it a nutrient worth including in a balanced diet. As with any health-related topic, it's essential to consider the overall body of evidence and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
8. Benefits for Eye Health
8. Benefits for Eye Health
Lycopene has also been linked to the promotion of eye health, particularly in relation to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and cataracts. AMD is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults, and cataracts are a common age-related eye condition that clouds the lens of the eye.
Studies have suggested that lycopene's antioxidant properties may help protect the eyes from oxidative stress, which is believed to contribute to the development of AMD and cataracts. Lycopene may also help reduce inflammation in the eyes, which can be a factor in these conditions.
In addition, lycopene has been found to accumulate in the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. This accumulation may help protect the macula from damage and support overall eye health.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between lycopene and eye health, incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet may be a beneficial strategy for maintaining healthy vision as you age.
Overall, the potential benefits of lycopene for eye health highlight the importance of a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, particularly those rich in lycopene. By supporting overall health and reducing inflammation, lycopene may play a role in promoting healthy vision and preventing age-related eye conditions.
9. Lycopene and Prostate Health
9. Lycopene and Prostate Health
Prostate health is a significant concern for men, particularly as they age. Lycopene has been the subject of numerous studies due to its potential role in maintaining prostate health and potentially reducing the risk of prostate cancer.
Research Findings:
- Several epidemiological studies have suggested that men with higher lycopene intakes have a lower risk of developing prostate cancer.
- A study published in the journal "Cancer Research" found that men with the highest intake of lycopene had a 21% reduced risk of prostate cancer compared to those with the lowest intake.
- Another study in the "Journal of the National Cancer Institute" indicated that men with higher blood levels of lycopene had a significantly lower risk of advanced prostate cancer.
Mechanism of Action:
- Lycopene's antioxidant properties may help protect the prostate from oxidative stress, which is believed to contribute to the development of prostate cancer.
- It has been suggested that lycopene may also modulate cell signaling pathways and gene expression related to cancer development.
Recommendations for Prostate Health:
- Incorporating lycopene-rich foods into the diet can be beneficial for prostate health.
- Foods such as tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit are excellent sources of lycopene.
- Cooking tomatoes, as in tomato sauce or soup, can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it more readily absorbed by the body.
It's important to note that while lycopene shows promise in supporting prostate health, it should not be considered a cure or a sole preventative measure for prostate cancer. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle are still essential components of maintaining overall prostate health. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is always recommended.
10. How to Increase Lycopene Intake
10. How to Increase Lycopene Intake
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that offers a myriad of health benefits. To increase your lycopene intake, consider incorporating the following strategies into your daily routine:
1. Eat More Tomatoes: As one of the richest sources of lycopene, tomatoes should be a staple in your diet. Fresh tomatoes, tomato sauce, and tomato paste are all excellent choices.
2. Cooked Tomatoes: Cooking tomatoes can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for your body to absorb. Try incorporating cooked tomato dishes like pasta sauces, soups, and stews into your meals.
3. Tomato Products: Canned tomatoes, tomato juice, and tomato sauce are also high in lycopene. These products can be easily added to various dishes to boost your intake.
4. Red-Colored Fruits and Vegetables: Besides tomatoes, other red-colored fruits and vegetables like watermelon, red grapefruit, and red bell peppers are also good sources of lycopene.
5. Cook with Healthy Oils: Lycopene is fat-soluble, which means it is better absorbed when consumed with a source of fat. Cooking with healthy oils like olive oil can enhance lycopene absorption.
6. Diversify Your Diet: Include a variety of lycopene-rich foods in your diet to ensure you are getting a good amount of this nutrient. This can include a mix of fruits, vegetables, and tomato-based products.
7. Supplements: If you find it challenging to get enough lycopene through your diet, consider taking a lycopene supplement. However, it's always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
8. Foods Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Consuming foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, can help increase the absorption of lycopene.
9. Avoid Overcooking: While cooking can increase lycopene bioavailability, overcooking can destroy it. Aim for gentle cooking methods to preserve the nutrient.
10. Regular Intake: Make lycopene-rich foods a regular part of your diet to ensure consistent intake and to maximize the health benefits.
By incorporating these strategies, you can effectively increase your lycopene intake and enjoy the numerous health benefits associated with this potent antioxidant. Remember, a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables is key to overall health and well-being.
11. Conclusion and Recommendations
11. Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, lycopene is a powerful carotenoid with a wide range of health benefits. Its unique chemical structure, characterized by its extensive conjugated double bond system, contributes to its potent antioxidant properties. Lycopene is found abundantly in red fruits and vegetables, with tomatoes being the richest source. Consuming lycopene-rich foods can provide numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, enhanced skin health, cancer prevention, and better eye health.
Lycopene's role in human health is multifaceted. It acts as a potent antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. This helps protect against various diseases and conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, certain types of cancer, and age-related macular degeneration. Lycopene also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
To increase lycopene intake, it is recommended to incorporate more lycopene-rich foods into your diet. These include tomatoes, watermelon, red grapefruit, guava, and papaya. Cooking tomatoes can increase the bioavailability of lycopene, making it easier for the body to absorb. Additionally, consuming these foods with a source of healthy fat, such as olive oil, can further enhance lycopene absorption.
While lycopene supplements are available, it is generally recommended to obtain lycopene through a balanced diet. Supplements may not provide the same benefits as consuming lycopene-rich foods, as they may lack other beneficial compounds found in whole foods.
In summary, lycopene is a valuable nutrient with numerous health benefits. By incorporating lycopene-rich foods into your diet, you can support your overall health and well-being. As always, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Purple Sweet Potato Extract
2023-09-28
-
Green coffee bean Extract
2023-09-28
-
Hawthorn Extract
2023-09-28
-
Almond Extract Powder
2023-09-28
-
Mango flavored powder
2023-09-28
-
Astaxanthin
2023-09-28
-
Peppermint Extract Powder
2023-09-28
-
Licorice Root Extract Powder
2023-09-28
-
Pine bark Extract Powder
2023-09-28
-
Red Date Extract
2023-09-28