- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
how much lycopene is in watermelon
2023-09-27

1. Lycopene Benefits
Lycopene Benefits
Lycopene is a powerful carotenoid antioxidant found in a variety of red-colored fruits and vegetables, including watermelon. It is known for its numerous health benefits, which can contribute to overall well-being and disease prevention. Here are some of the key benefits of lycopene:
1. Heart Health: Lycopene has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. It helps to lower bad cholesterol levels and blood pressure, which can lead to a healthier cardiovascular system.
2. Cancer Prevention: Studies have suggested that lycopene may play a role in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate, lung, and stomach cancers. Its antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals that can damage cells and lead to cancer.
3. Skin Health: Lycopene can protect the skin from harmful UV rays and reduce the risk of sunburn. It also helps to maintain skin elasticity and reduce the signs of aging.
4. Eye Health: The antioxidant properties of lycopene can protect the eyes from age-related macular degeneration and cataracts.
5. Anti-Inflammatory: Lycopene has anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body, which is beneficial for conditions like arthritis.
6. Immune System Support: Lycopene can help strengthen the immune system by protecting the body from infections and diseases.
7. Bone Health: Some research indicates that lycopene may help maintain bone health by improving bone mineral density.
8. Neuroprotection: Lycopene may also have neuroprotective effects, potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's.
By incorporating foods rich in lycopene, such as watermelon, into your diet, you can enjoy these health benefits and support a healthier lifestyle.
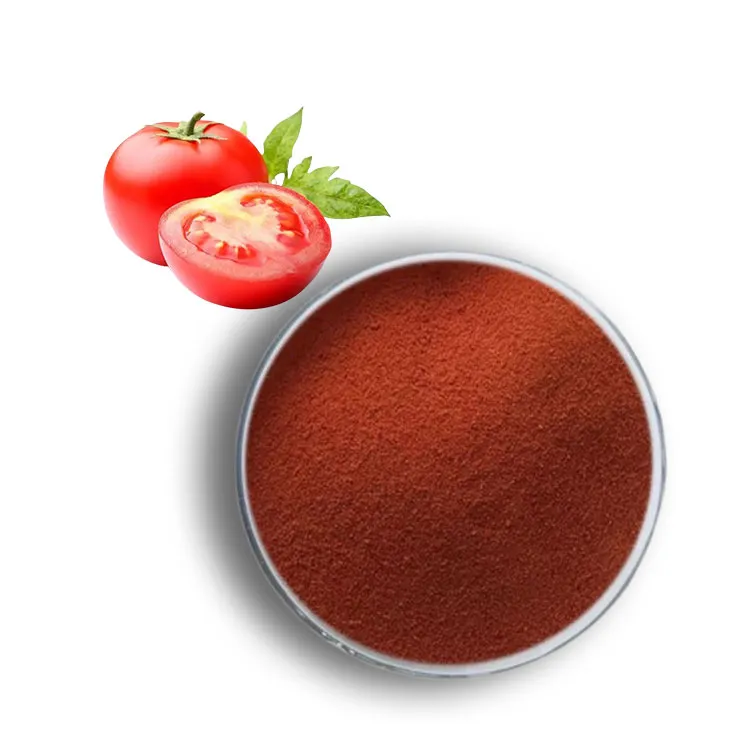
2. Watermelon as a Source of Lycopene
2. Watermelon as a Source of Lycopene
Watermelon, a popular fruit enjoyed by many around the globe, is not only a refreshing and sweet treat but also a rich source of lycopene. Known for its vibrant red color and juicy texture, watermelon is a staple in many diets, especially during the summer months. However, its nutritional value extends beyond its delicious taste and cooling properties.
Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that belongs to the carotenoid family. It is responsible for the red coloration found in various fruits and vegetables, including tomatoes and watermelon. This nutrient has been linked to numerous health benefits, such as reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, promoting heart health, and supporting healthy skin.
Watermelon contains a significant amount of lycopene, particularly in its flesh. The concentration of lycopene in watermelon can vary depending on factors such as the variety of watermelon, ripeness, and growing conditions. Nevertheless, it is a valuable source of this beneficial compound.
One of the advantages of watermelon as a source of lycopene is its high water content. This makes it an easily digestible and hydrating option for those looking to increase their lycopene intake. Additionally, watermelon is low in calories and rich in other essential nutrients, such as vitamins A and C, making it a nutritious and guilt-free choice.
In conclusion, watermelon is an excellent source of lycopene, offering a natural and enjoyable way to boost your intake of this important antioxidant. Its refreshing taste and high water content make it a popular choice for those seeking a healthy and delicious way to improve their overall well-being.
3. Lycopene Content in Watermelon
3. Lycopene Content in Watermelon
Watermelon is a delightful fruit that not only provides a refreshing taste and a juicy texture but also packs a powerful punch of nutrients, particularly lycopene. Lycopene is a potent antioxidant and a phytochemical that belongs to the carotenoid family. It is known for its numerous health benefits, and watermelon is one of the richest dietary sources of this nutrient.
The lycopene content in watermelon can vary depending on several factors such as the variety of watermelon, ripeness, and growing conditions. However, on average, watermelon contains a significant amount of lycopene. According to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), a one-cup serving of diced watermelon (approximately 154 grams) contains about 9.67 milligrams of lycopene.
It is important to note that the lycopene content is not evenly distributed throughout the watermelon. The flesh of the watermelon, which is typically consumed, contains a moderate amount of lycopene. However, the rind or the white part of the watermelon, which is often discarded, contains a higher concentration of lycopene. In fact, the rind can have up to three times more lycopene than the flesh.
While the exact amount of lycopene in watermelon can vary, it is clear that watermelon is a valuable source of this nutrient. Incorporating watermelon into your diet can provide you with a natural and delicious way to boost your lycopene intake.
In the next section, we will discuss the factors that can affect the absorption of lycopene from watermelon and how you can maximize its bioavailability.
4. Factors Affecting Lycopene Absorption
4. Factors Affecting Lycopene Absorption
Lycopene is a fat-soluble nutrient, which means that its absorption in the body is influenced by the presence of dietary fats. Several factors can affect the amount of lycopene that your body absorbs from watermelon or other sources:
4.1 Presence of Dietary Fat
The most significant factor affecting lycopene absorption is the presence of dietary fat. Consuming watermelon with a source of healthy fats, such as avocado, nuts, or olive oil, can enhance lycopene absorption. This is because fats help in the emulsification of lycopene, making it more bioavailable for absorption.
4.2 Cooking Methods
Cooking can also impact lycopene absorption. Some studies suggest that cooking tomatoes and tomato-based products can increase the bioavailability of lycopene. The heat from cooking can break down cell walls, releasing lycopene and making it more accessible for absorption. While watermelon is typically consumed raw, understanding this principle can be helpful when incorporating cooked tomato products into your diet.
4.3 Variety of Watermelon
Different varieties of watermelon can contain varying amounts of lycopene. Generally, red-fleshed watermelons have higher lycopene content than yellow-fleshed varieties. Additionally, the ripeness of the watermelon can influence lycopene levels, with riper fruits typically having more lycopene.
4.4 Processing
Processing watermelon into juice or paste can also impact lycopene absorption. Some studies have shown that consuming watermelon juice can lead to higher serum lycopene levels compared to eating whole watermelon. This may be due to the increased bioaccessibility of lycopene when the fruit is processed.
4.5 Individual Differences
Individual differences in metabolism, gut health, and overall diet can also affect how much lycopene is absorbed. People with certain health conditions or those taking specific medications may have altered lycopene absorption.
4.6 Other Nutrients
The presence of other nutrients, such as vitamin E and selenium, can also influence lycopene absorption. These nutrients work synergistically to enhance the antioxidant effects of lycopene and improve its bioavailability.
Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about how to maximize lycopene absorption from watermelon and other dietary sources. By incorporating a variety of these strategies, you can ensure that you are getting the most health benefits from this powerful antioxidant.
5. How to Maximize Lycopene Intake
5. How to Maximize Lycopene Intake
To maximize the lycopene intake from watermelon, it's essential to understand the factors that can influence its bioavailability and absorption. Here are some strategies to help you get the most out of this powerful antioxidant:
1. Choose ripe watermelons: Lycopene content is higher in ripe fruits. Look for watermelons with a deep green rind, free of cuts or bruises, and a dull sound when knocked.
2. Eat with a bit of fat: Lycopene is fat-soluble, which means it's better absorbed when consumed with a small amount of fat. Pair your watermelon with a drizzle of olive oil, a handful of nuts, or a bit of avocado.
3. Incorporate into smoothies: Blending watermelon with other fruits and vegetables can increase the bioavailability of lycopene. Adding a source of healthy fat, like avocado or flaxseed oil, can further enhance absorption.
4. Cook with it: Cooking watermelon can break down cell walls, making lycopene more accessible for absorption. Try grilling or roasting watermelon to unlock its full potential.
5. Consume regularly: Regular consumption of watermelon can help maintain a steady supply of lycopene in your body. Aim to include watermelon in your diet a few times a week.
6. Opt for watermelon products: If fresh watermelon isn't available, consider watermelon juice or dried watermelon snacks. These options can still provide a good amount of lycopene.
7. Combine with other lycopene-rich foods: To boost your lycopene intake, combine watermelon with other foods high in lycopene, such as tomatoes, red bell peppers, and pink grapefruit.
8. Be mindful of processing: Over-processing can reduce the lycopene content in watermelon. Choose fresh, minimally processed options whenever possible.
9. Store properly: Keep watermelon at room temperature for maximum lycopene content. Refrigeration can affect the fruit's texture and flavor, but if you must refrigerate, store it in a cool, dry place.
10. Enjoy the rind: The rind of the watermelon contains lycopene as well. You can pickle the rind or use it in salads to increase your lycopene intake.
By following these tips, you can ensure that you're getting the most out of watermelon's lycopene content and reaping its numerous health benefits. Remember, moderation and variety are key to a balanced diet, so enjoy watermelon as part of a diverse array of fruits and vegetables.
6. Health Risks and Precautions
6. Health Risks and Precautions
While watermelon and lycopene are generally considered safe and beneficial for health, it is important to be aware of potential risks and precautions when consuming them in large quantities or in certain situations.
1. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to watermelon or other melons. Symptoms can range from mild, such as itching or hives, to severe, including difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis. If you have a known allergy to watermelon, it is best to avoid it.
2. Excessive Intake: Consuming large amounts of watermelon, especially if it is the primary source of lycopene in your diet, can lead to excessive sugar intake. This is because watermelon is high in natural sugars. Overconsumption can contribute to weight gain and blood sugar issues, particularly for those with diabetes.
3. Interactions with Medications: Certain medications may interact with the compounds found in watermelon. For example, watermelon can affect the way your body processes certain drugs, potentially altering their effectiveness or causing adverse effects.
4. Kidney Issues: Watermelon is high in potassium, which is generally beneficial for health. However, individuals with kidney problems may need to limit their intake of potassium-rich foods, including watermelon, to avoid complications.
5. Citrus Red No. 2: Some watermelons are treated with a dye called Citrus Red No. 2 to enhance their appearance. While it is approved for use in the United States, it has been banned in the European Union due to potential health concerns. If avoiding artificial dyes is a concern for you, look for untreated watermelons.
6. Potential for Pesticide Residue: Like many fruits, watermelons can be treated with pesticides. While these are generally considered safe when used as directed, some individuals may prefer to opt for organic watermelons to minimize exposure to these chemicals.
7. Hydration and Water Intake: While watermelon is high in water content and can contribute to hydration, it should not replace drinking water. Ensure you are consuming adequate water throughout the day to maintain proper hydration levels.
8. Portion Control: Enjoy watermelon as part of a balanced diet. Overeating any food, including watermelon, can lead to imbalances in your diet and potential health issues.
In conclusion, while watermelon is a delicious and nutritious fruit rich in lycopene, it is important to consume it in moderation and be aware of any potential risks or interactions with your individual health conditions or medications. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your diet and specific food choices.
7. Conclusion
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, watermelon is a delicious and refreshing fruit that offers a variety of health benefits, particularly due to its high lycopene content. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that can help protect against various diseases, including heart disease and certain types of cancer. While watermelon is a rich source of lycopene, the exact amount can vary depending on factors such as variety, ripeness, and processing methods.
To maximize lycopene intake, it's important to choose ripe, red-fleshed watermelons and consume them in a way that enhances lycopene absorption, such as with a little fat or through cooking. However, it's also important to be aware of potential health risks and precautions, such as the possibility of an allergic reaction or the risk of excessive fructose intake.
Overall, incorporating watermelon into a balanced diet can be a tasty and nutritious way to boost your lycopene intake and support your overall health. So, the next time you're in the mood for a refreshing and healthy snack, consider reaching for a slice of watermelon and enjoy the many benefits it has to offer.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Hops Extract
2023-09-27
-
Hawthorn Extract
2023-09-27
-
Genistein
2023-09-27
-
Diosmin
2023-09-27
-
Lycopene
2023-09-27
-
Black Garlic Extract
2023-09-27
-
Tormentil Extract
2023-09-27
-
Garcinia Cambogia Extract
2023-09-27
-
Feverfew Extract
2023-09-27
-
Plantain extract
2023-09-27