- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Is quercetin the same as bioflavonoids?
2025-07-20

The realm of natural health comprises a plethora of compounds, each revered for its potential benefits to human wellness. Among these compounds, Quercetin and bioflavonoids frequently find themselves grouped together due to their overlapping properties and effects. However, while they share similarities, Quercetin and bioflavonoids are distinct entities with unique attributes and specific health implications. This comprehensive article explores the nuances between Quercetin and bioflavonoids, shedding light on their differences, similarities, and respective benefits in promoting health and well-being.
Understanding Quercetin
Quercetin is a type of flavonoid—specifically, a flavonol—found naturally in a variety of fruits, vegetables, and grains. It stands out for its robust antioxidant activity and plays a critical role in protecting cells against oxidative damage. Quercetin's widespread availability in foods such as apples, onions, berries, broccoli, and tea makes it a staple in a balanced diet. With its anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anticancer properties, quercetin is gaining substantial attention in the field of nutrition and medicine.
Key Benefits of Quercetin:
1. Antioxidant Properties: Quercetin helps neutralize free radicals, reducing oxidative stress and lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and cancer.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Effects: It inhibits inflammatory pathways, aiding in the management of conditions like arthritis and allergies.
3. Immune System Support: Quercetin boosts immune defense by modulating immune response, making it useful during viral infections.
4. Circulatory Health: It improves blood vessel function and helps prevent cardiovascular disorders by reducing the risk of artery hardening and plaque formation.
5. Exercise Performance: Studies suggest quercetin can enhance physical endurance and reduce exercise-induced fatigue.

Exploring Bioflavonoids
Bioflavonoids, often simply referred to as flavonoids, comprise a broad class of plant-based polyphenolic compounds. These compounds are responsible for the vivid colors in fruits and vegetables and contribute to their flavor and health-promoting properties. Bioflavonoids encompass various types, including flavanones, flavones, flavonols (like quercetin), anthocyanins, and catechins, each offering specific health benefits.
Bioflavonoids are vital for plant survival, exerting functions such as UV filtration, symbiotic nitrogen fixation, and acting as chemical messengers. In human nutrition, they are celebrated for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capabilities, among other benefits.
Key Benefits of Bioflavonoids:
1. Antioxidant Action: Bioflavonoids protect against oxidative stress, reducing cell damage and supporting longevity.
2. Cardiovascular Health: They aid in managing hypertension, reducing cholesterol, and preventing atherosclerosis.
3. Metabolic Support: Bioflavonoids enhance glucose metabolism and support weight management.
4. Cancer Protection: Their ability to modulate carcinogenic pathways offers a protective effect against certain cancers.
5. Skin Health: Bioflavonoids improve skin elasticity and provide protection against UV-mediated damage.

Quercetin vs. Bioflavonoids: Similarities and Differences
Similarities:
Both quercetin and bioflavonoids belong to the larger flavonoid family, sharing fundamental biochemical structures. As part of this family, they exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, contributing to various health benefits. Their presence in plant-based foods underlines the importance of a diet rich in fruits and vegetables for optimal health.
Differences:
1. Classification: Quercetin is a specific type of bioflavonoid, whereas the term "bioflavonoids" encompasses a broader group of various flavonoid types.
2. Diversity: Bioflavonoids include multiple subtypes beyond just flavonols, offering a wider array of health effects. Quercetin, while versatile, focuses on specialized benefits.
3. Concentration in Foods: Quercetin is concentrated in specific foods such as apples and onions, while bioflavonoids like anthocyanins are predominant in berries and flavanones in citrus fruits.
4. Health Focus: Quercetin’s research is often directed towards specific functions like immune modulation and antiviral activity, whereas bioflavonoids cover broader health areas including metabolic health and skin protection.
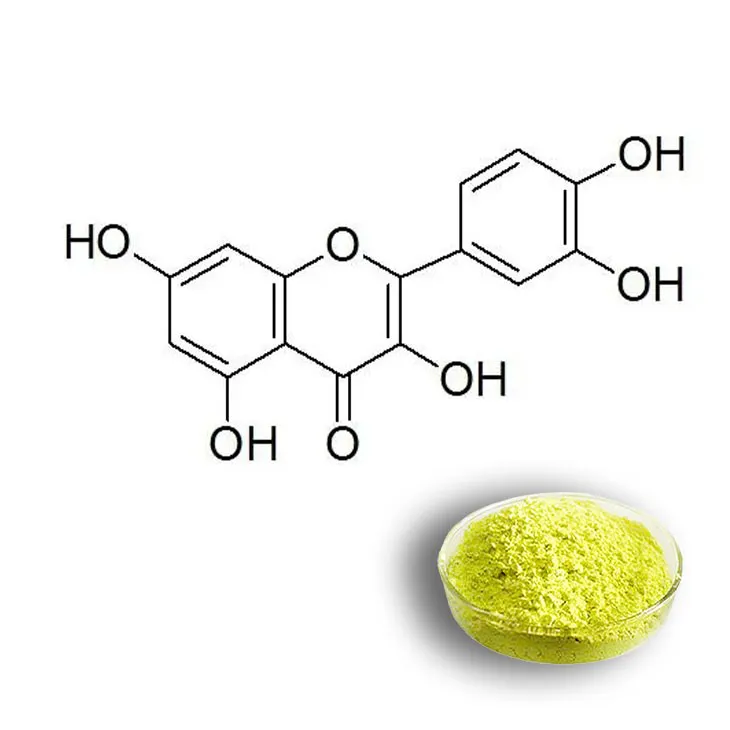
The Therapeutic Applications of Quercetin and Bioflavonoids
The pharmacological properties of quercetin and bioflavonoids open avenues for numerous therapeutic applications supporting overall health.
Quercetin in Immune Health:
Quercetin is utilized in therapeutic settings to support immune function and mitigate allergy symptoms. Its ability to regulate histamine release makes it beneficial for individuals with allergic conditions.
Bioflavonoids in Cardiovascular Health:
Bioflavonoids are included in formulations targeting cardiovascular health, utilizing their ability to manage cholesterol levels and improve endothelial function.
Joint Health Support:
Both quercetin and bioflavonoids are incorporated into joint health supplements, reducing inflammation and aiding mobility in conditions such as arthritis.
Metabolic Health:
Bioflavonoids play a role in weight management supplements due to their effects on glucose metabolism and fat oxidation.

Practical Advice for Incorporating Quercetin and Bioflavonoids into Your Diet
Maximizing health benefits involves conscious dietary choices that emphasize foods rich in quercetin and bioflavonoids. Here are practical ways to incorporate them:
1. Diversify fruit and vegetable intake: Regular consumption of apples, onions, berries, citrus fruits, and green leafy vegetables ensures a varied intake of quercetin and bioflavonoids.
2. Consider supplements: If dietary sources are limited, quercetin and bioflavonoid supplements can provide additional support. Always choose high-quality products and consult healthcare professionals for guidance.
3. Include herbal teas: Black tea and green tea are excellent sources of flavonoids, offering both quercetin and catechins.
Cautions and Considerations
While quercetin and bioflavonoids are generally safe for most individuals, responsible consumption is advised, particularly concerning supplements. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should seek medical advice before using concentrated forms. Individuals with medical conditions or taking other medications should consult healthcare providers to prevent interactions.
Conclusion
Quercetin and bioflavonoids are powerful allies in maintaining and enhancing health, offering complementary benefits that support immunity, cardiovascular wellness, joint health, and more. Understanding their unique and overlapping effects provides clarity in choosing effective nutritional strategies and supplements.
Incorporating a variety of flavonoid-rich foods into daily dietary practices paves the way for comprehensive health support, promoting well-being and longevity. As research continues to explore the depths of these natural compounds, their relevance in health regimes grows, underscoring the significance of consuming adequate plant-based nutrients for optimal health. By equipping consumers with knowledge about these key health compounds, individuals can make informed choices that elevate their wellness journey.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Red Vine Extract
2025-07-20
-
Pomegranate Extract
2025-07-20
-
Saffron Extract Powder
2025-07-20
-
Green Tea Extract
2025-07-20
-
Yohimbine Bark Extract
2025-07-20
-
Cassia Seed Extract
2025-07-20
-
Panax Ginseng Leaf Extract
2025-07-20
-
Coix Seed Extract
2025-07-20
-
Kupilu Extract
2025-07-20
-
Peppermint Oil
2025-07-20





















