- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Why is astaxanthin so powerful?
2025-06-26
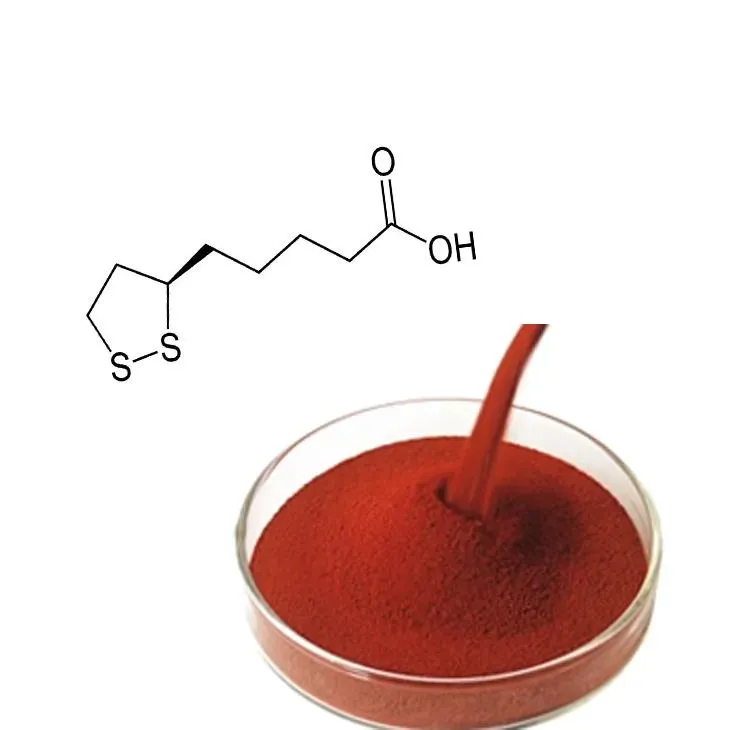
Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid pigment that has gained attention for its powerful antioxidant properties. Often dubbed the "king of carotenoids," Astaxanthin is responsible for the vibrant red and pink hues found in organisms such as salmon, shrimp, and flamingos. This article explores why Astaxanthin is considered one of the most powerful antioxidants, the science behind its benefits, and its potential applications in promoting human health.
Understanding Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin belongs to a larger family of carotenoids, which are pigments found in plants and certain types of sea life. Unlike other carotenoids like beta-carotene, astaxanthin does not convert into vitamin A in the human body. Instead, it provides a wide range of health benefits that have made it a popular supplement. Derived predominantly from microalgae (Haematococcus pluvialis), astaxanthin becomes concentrated in the organisms that feed on these algae, such as krill and salmon, thus making its way into the human diet.
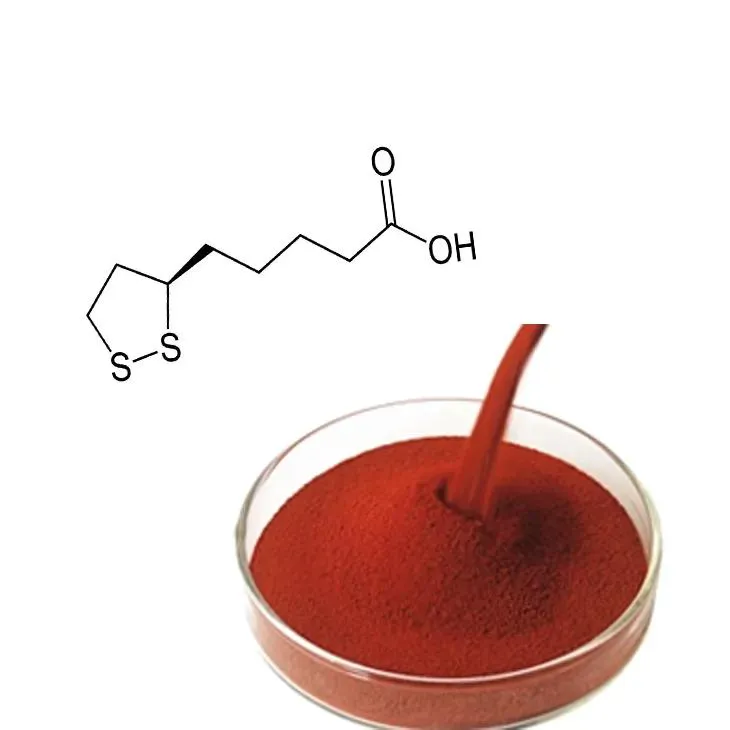
Potent Antioxidant Capabilities
Astaxanthin is renowned for its extraordinary antioxidant capacity. It has been found to be significantly more potent than other carotenoids and antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, and CoQ10. The unique molecular structure of astaxanthin allows it to neutralize free radicals and protect cells from oxidative stress and damage more effectively. This robustness is due to astaxanthin's ability to span the cell membrane, providing comprehensive protection both inside and outside the cell.

The Role of Astaxanthin in Combating Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Over time, excessive oxidative stress can lead to cellular damage and contribute to a variety of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Astaxanthin's powerful antioxidant properties make it effective in scavenging free radicals and mitigating oxidative damage, thereby supporting overall health and longevity.
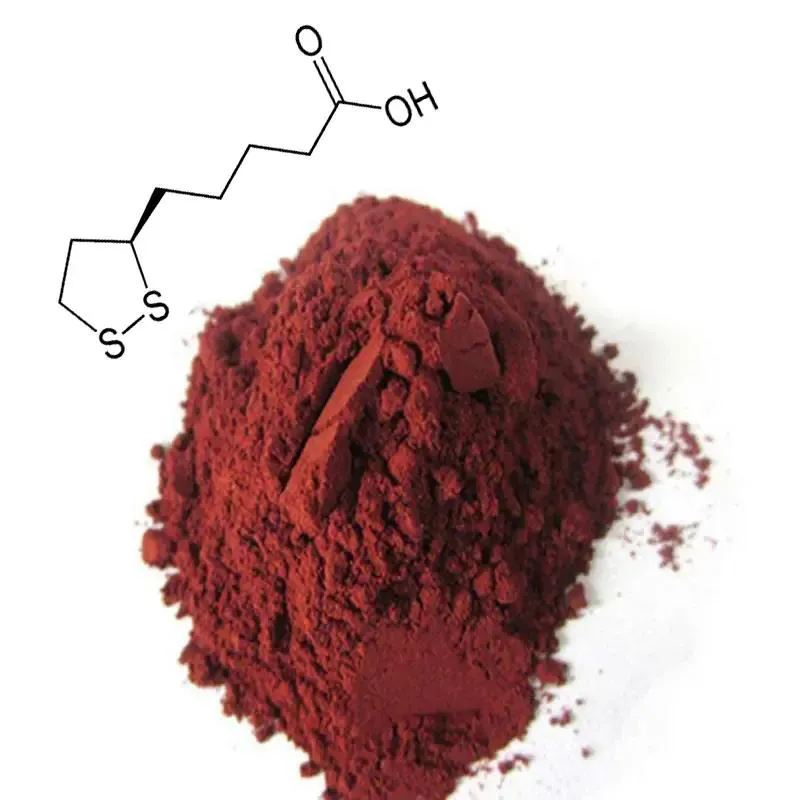
Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
1. Cardiovascular Health
Astaxanthin supports cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving lipid profiles, and enhancing blood flow. Studies have shown that astaxanthin can help lower levels of LDL cholesterol (often referred to as “bad” cholesterol) and increase HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol). Furthermore, it may prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, a key contributor to atherosclerosis, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease.
2. Skin Health
One of the most popular applications of astaxanthin is in skin health. Its antioxidant properties protect skin cells from damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation and environmental pollutants. Clinical studies have demonstrated that astaxanthin supplementation can improve skin elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and enhance skin hydration. By neutralizing free radicals, astaxanthin helps slow down the aging process of the skin, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
3. Eye Health
Astaxanthin's protective effects extend to ocular health. It has the ability to cross the blood-retinal barrier and protect eye tissues from oxidative damage. This has implications for reducing the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other degenerative eye disorders. Astaxanthin may also relieve eye fatigue and improve visual acuity.
4. Exercise Performance and Recovery
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts often turn to astaxanthin to enhance exercise performance and recovery. Its anti-inflammatory properties help reduce muscle damage and soreness after intense physical activity. Astaxanthin's ability to improve mitochondrial function also supports enhanced energy production and endurance, promoting overall athletic performance.
5. Cognitive Health
Astaxanthin’s antioxidant properties are beneficial for brain health, particularly in protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in neural tissues, astaxanthin may play a role in maintaining cognitive function and preventing age-related cognitive decline.
6. Immune System Support
Astaxanthin enhances immune function by modulating the activity of immune cells and reducing inflammatory responses. Its immunomodulatory effects can help prevent infections and support the body's natural defense mechanisms.
Potential and Emerging Uses
The versatility of astaxanthin suggests potential applications beyond the currently recognized health benefits. Emerging research is investigating astaxanthin's role in cancer prevention, metabolic syndrome, fertility, and more. While findings are promising, further clinical studies are needed to substantiate these claims and explore new therapeutic avenues.
Considerations and Safe Use
Astaxanthin is generally considered safe and well tolerated when taken within suggested dosages. However, as with any supplement, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before starting astaxanthin, especially for individuals who are pregnant, nursing, or have underlying health conditions. Additionally, choosing a high-quality supplement from a reputable source ensures purity and efficacy.
Conclusion
Astaxanthin's impressive antioxidant capabilities and its wide range of health benefits make it a powerful tool for promoting wellness. From cardiovascular and skin health to cognitive and immune support, astaxanthin has demonstrated incredible efficacy in protecting the body against oxidative stress and maintaining overall health. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this remarkable compound, astaxanthin stands out as a valuable addition to a health-conscious lifestyle, offering natural and robust protection in the quest for longevity and quality of life.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Black Garlic Extract
2025-06-26
-
Konjac Powder
2025-06-26
-
Black Pepper Extract
2025-06-26
-
Bitter Melon Extract
2025-06-26
-
Apricot Powder
2025-06-26
-
Camu Camu Extract
2025-06-26
-
Clove Powder
2025-06-26
-
Lily extract
2025-06-26
-
Dandelion Leaf Extract
2025-06-26
-
Nettle Root Extract
2025-06-26





















