- 0086-571-85302990
- sales@greenskybio.com
Choosing the Best Form of Astaxanthin: A Guide for Consumers
2025-06-26
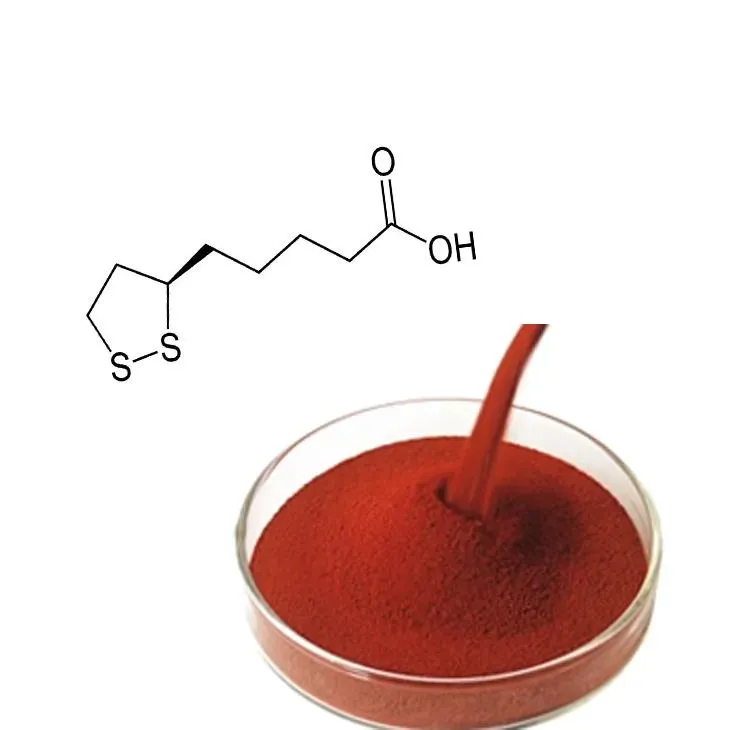
Astaxanthin, a naturally occurring carotenoid, has gained recognition for its potent antioxidant properties and wide-ranging health benefits. Found in algae, yeast, salmon, trout, krill, shrimp, and crayfish, this vibrant red pigment is responsible for the striking pink or red color seen in these organisms. As a dietary supplement, Astaxanthin is prized for its potential to support skin health, reduce inflammation, enhance athletic performance, and more. However, with several forms of Astaxanthin available on the market, consumers often face the challenge of determining which form is the most effective. This article explores the various forms of astaxanthin and offers guidance on choosing the best option for your needs.
Understanding Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is classified as a xanthophyll, a subclass of carotenoids, and is known as one of the most powerful antioxidants found in nature. Its structure allows it to effectively neutralize free radicals, protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is associated with aging and chronic diseases.
Due to its antioxidant capacity, astaxanthin is often marketed for several health benefits, including improved skin health and protection against UV damage, reduced inflammation and joint support, enhanced eye health, boosted immune function, and increased endurance and recovery in athletes.
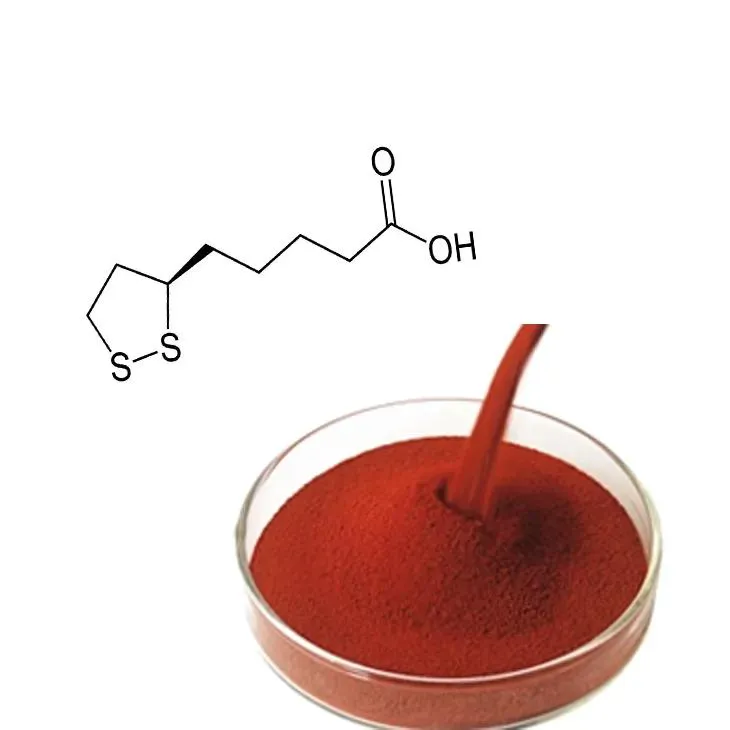
Natural vs. Synthetic Astaxanthin
When it comes to choosing astaxanthin supplements, the primary consideration is whether to opt for natural or synthetic forms. Understanding their differences can significantly impact effectiveness and health outcomes.
Natural Astaxanthin
Natural astaxanthin is typically extracted from the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis, known for its high concentration of this carotenoid. This form of astaxanthin is touted for its superior antioxidant properties and bioavailability, making it a popular choice among consumers seeking maximum health benefits.
Several sources of natural astaxanthin include microalgae (Haematococcus pluvialis), which is the most common and commercially viable source of astaxanthin, yeast (Phaffia rhodozyma), which offers astaxanthin produced through fermentation, and seafood, where astaxanthin is obtained through the diet of marine animals like salmon and krill.
Synthetic Astaxanthin
Synthetic astaxanthin is chemically produced and is primarily used in animal feed, particularly in aquaculture, to provide the characteristic pink color to farmed salmon. Although available as a dietary supplement, synthetic astaxanthin is generally less effective than its natural counterpart due to differences in its molecular structure which affect its biological activity.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Astaxanthin
Bioavailability: Natural astaxanthin from Haematococcus pluvialis scores high in bioavailability, meaning it is more easily absorbed and utilized by the body compared to synthetic versions. This translates to more effective antioxidant action and better health outcomes.
Purity and Source: Opt for supplements that clearly state the source of astaxanthin, with preference given to those derived from natural algae. Trusted brands undergo rigorous testing for purity, ensuring they are free from contaminants like heavy metals and solvents.
Product Formulation: Astaxanthin supplements are available in various formulations, including soft gels, capsules, and powders. Soft gels often have added oils which can enhance absorption of this fat-soluble carotenoid. Consider choosing a formulation that aligns with your dietary preferences and needs.
Concentration and Dosage: Products vary widely in concentration and recommended dosages. Effective amounts generally range from 4 mg to 12 mg per day. It's essential to follow manufacturer guidelines or consult a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for individual health goals.
Manufacturer Reputation: Purchasing from reputable manufacturers who prioritize quality assurance is crucial. Look for products with third-party certifications that verify ingredient authenticity and concentrations, ensuring supplementation safety and efficacy.
Conclusion: What Is the Best Form of Astaxanthin?
After evaluating various factors, natural astaxanthin extracted from Haematococcus pluvialis is widely considered the superior choice for supplementation. Its enhanced bioavailability, potent antioxidant properties, and extensive research supporting its health benefits make it an attractive option for consumers.
Before beginning any supplement regimen, including astaxanthin, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking other medications. With the right choice, astaxanthin can be a valuable addition to a balanced diet, offering numerous benefits that contribute to overall wellness.
In summary, when selecting an astaxanthin supplement, focus on natural sources, appropriate formulation, and reputable brands to maximize health benefits. This strategic choice will ensure that you harness the full potential of this powerful antioxidant, supporting your health and well-being in multifaceted ways.
- ▶ Hesperidin
- ▶ Citrus Bioflavonoids
- ▶ Plant Extract
- ▶ lycopene
- ▶ Diosmin
- ▶ Grape seed extract
- ▶ Sea buckthorn Juice Powder
- ▶ Fruit Juice Powder
- ▶ Hops Extract
- ▶ Artichoke Extract
- ▶ Mushroom extract
- ▶ Astaxanthin
- ▶ Green Tea Extract
- ▶ Curcumin
- ▶ Horse Chestnut Extract
- ▶ Other Product
- ▶ Boswellia Serrata Extract
- ▶ Resveratrol
- ▶ Marigold Extract
- ▶ Grape Leaf Extract
- ▶ New Product
- ▶ Aminolevulinic acid
- ▶ Cranberry Extract
- ▶ Red Yeast Rice
- ▶ Red Wine Extract
-
Yohimbine Bark Extract
2025-06-26
-
Grapefruit Seed Extract Powder
2025-06-26
-
Phellodendron Extract
2025-06-26
-
Angelica sinensis extract
2025-06-26
-
Black Garlic Extract
2025-06-26
-
Ivy Extract
2025-06-26
-
Longan Extract
2025-06-26
-
Fenugreek Extract Powder
2025-06-26
-
Withania Somnifera Extract
2025-06-26
-
Black Rice Extract
2025-06-26





















